A zero-click search is when someone Googles a question and receives the answer right away, without needing to click or visit any other websites–including yours.
This sits at odds with Google’s original search model, which worked by passing on referral traffic to third-party sites.
Google is getting better at creating zero-click searches, and that means that websites get fewer and fewer clicks in search.
Zero-click searches have been building for years. SERP features laid the groundwork, but AI has delivered the knockout punch.
March’s Core Update was the real tipping point: AI Overviews doubled overnight.
According to our research, they currently capture 18.9% of all US keywords–but for logged-in SERPs that figure is likely much higher.
Now that AI Mode has rolled out, the damage is accelerating.
Back in 2024, SparkToro found that 60% of all Google searches ended without a click.
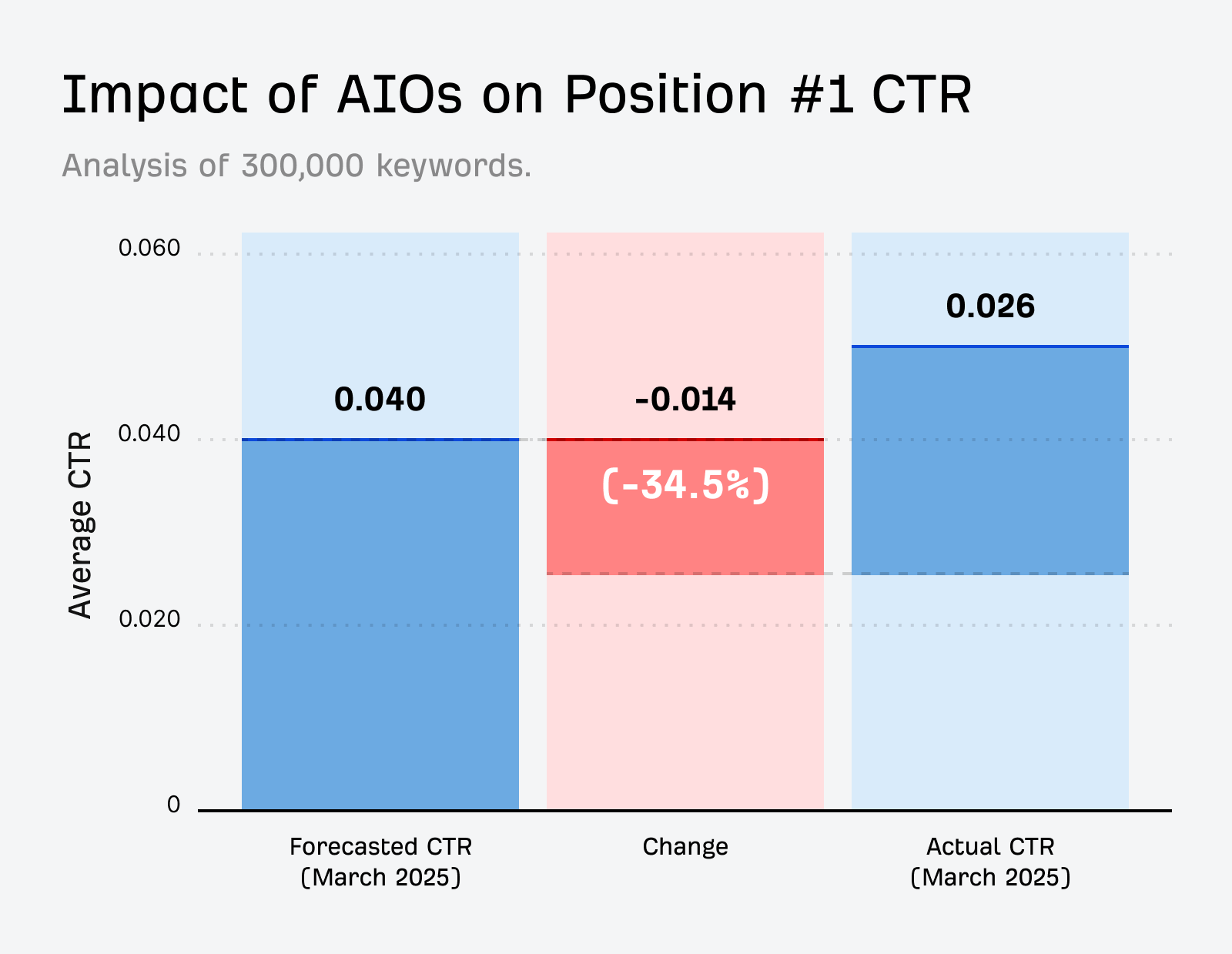
In 2025, our research shows AI summaries alone can slash clicks by 34.5%, with informational content taking the biggest hit.
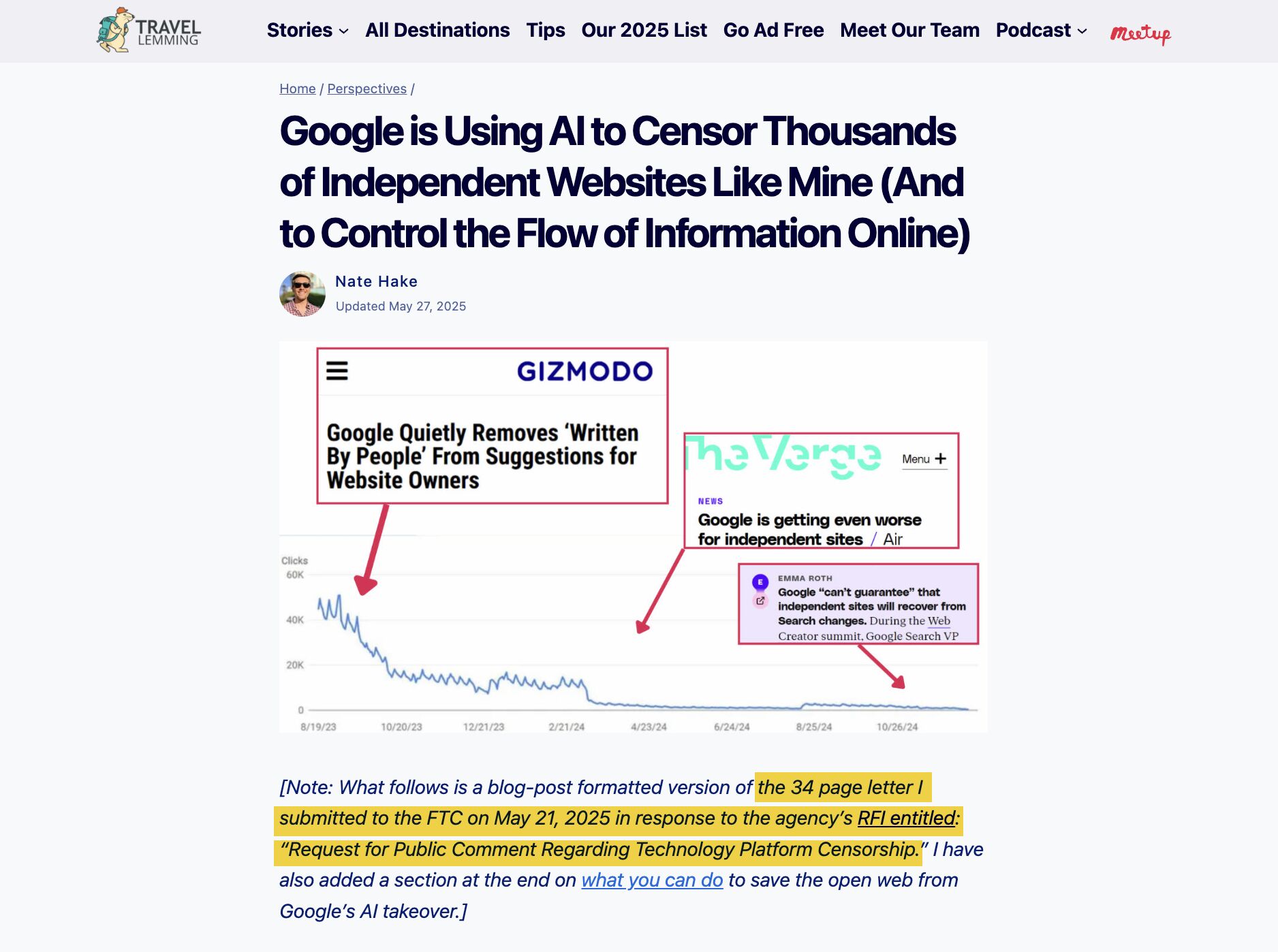
Lately, I have seen many sites lose substantial traffic on informational content and move quickly to diversify.
Most recently, Databox and Seer Interactive have reported significant organic traffic drops.
We’re all watching “the great decoupling” play out in our Google Search Console data–impressions count for double, while clicks nosedive.
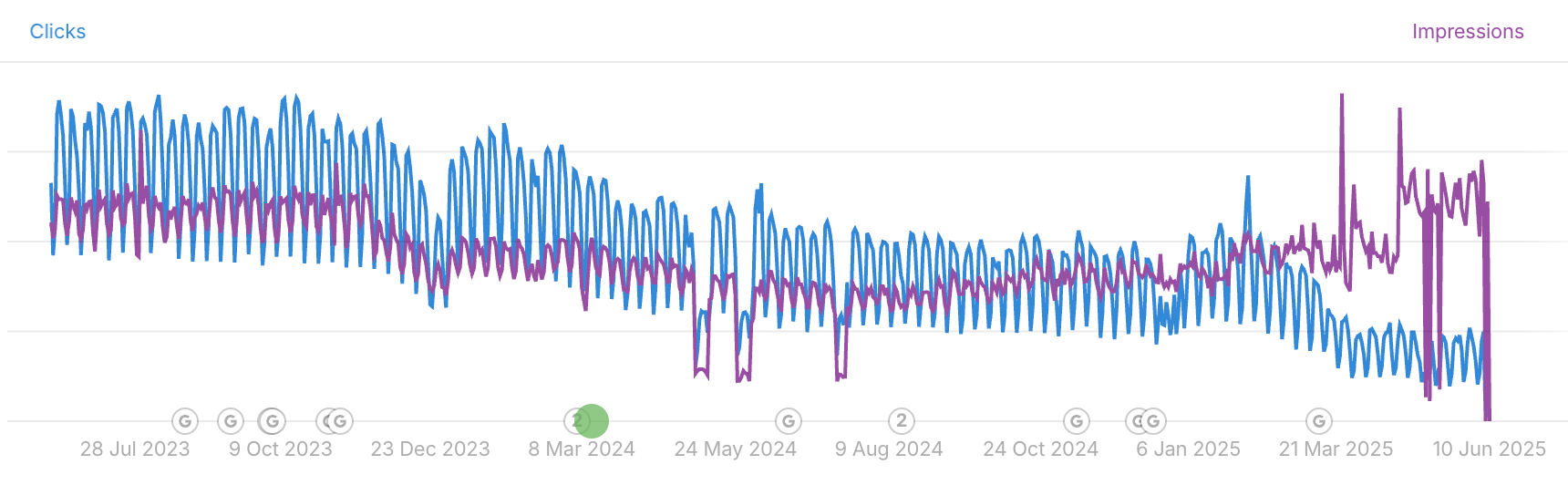
And that’s just from AI Overviews.
Soon, search will be a fully conversational interface, where getting clicked becomes the exception—not the rule.
Clickless search isn’t a new development.
Google has been claiming our clicks as far back as 2001, with the first SERP feature: Images.
But AI Overviews and AI Mode represent something different. They’re not just features, they’re fundamental changes to how search works.
Here’s what you need to know about the search features making a smash-and-grab for your clicks.
AI Overviews
AI Overviews are the AI generated summaries that show up at the top of search results. They deliver quick answers with information synthesized from different webpages.
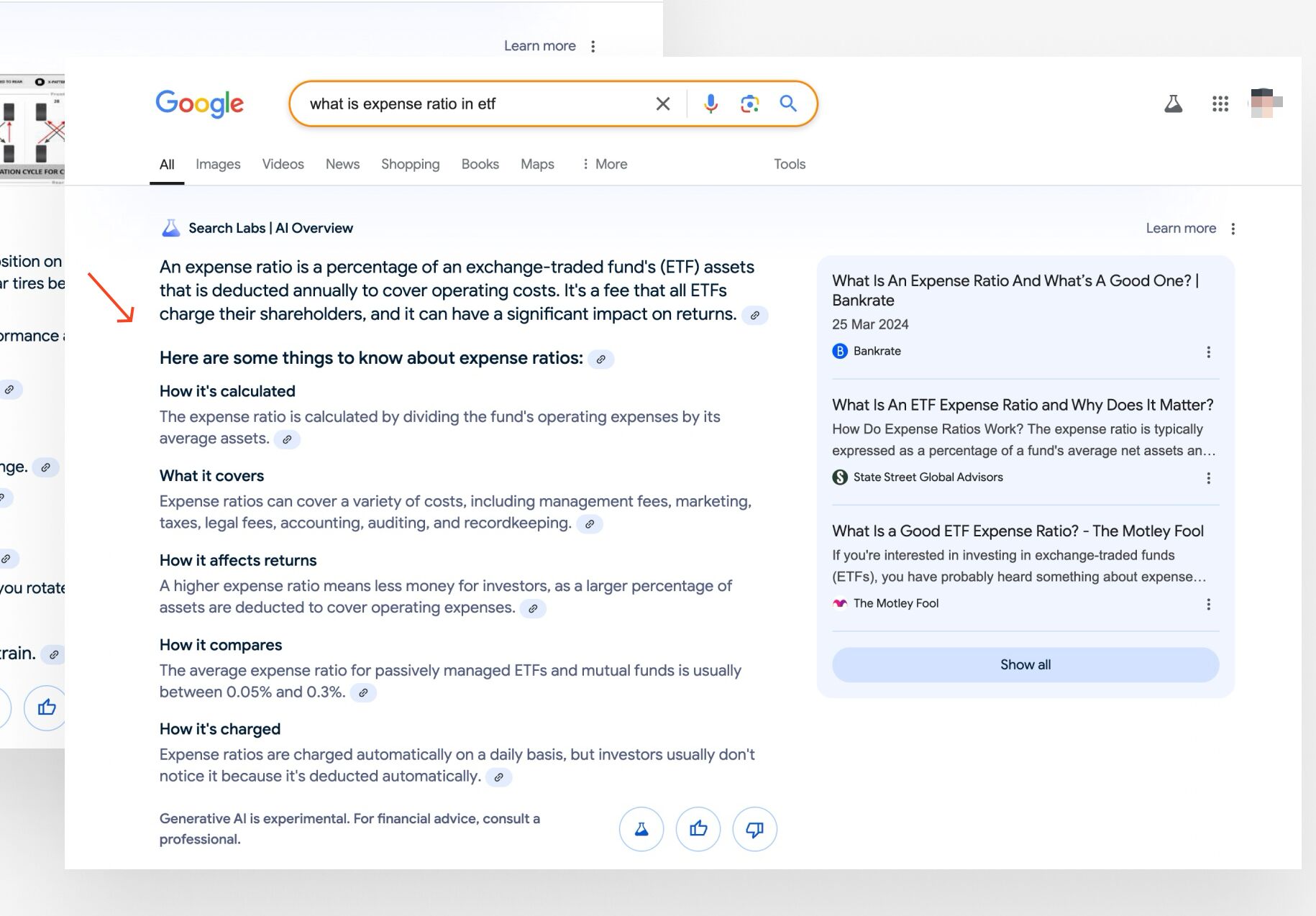
They began appearing for questions and long-tail queries, but they’re now a regular feature on stem keyword searches.
In fact, ironically, the phrases “AI Overviews” and “Zero-click search” have acquired an AI Overview in the time it has taken me to write this article.
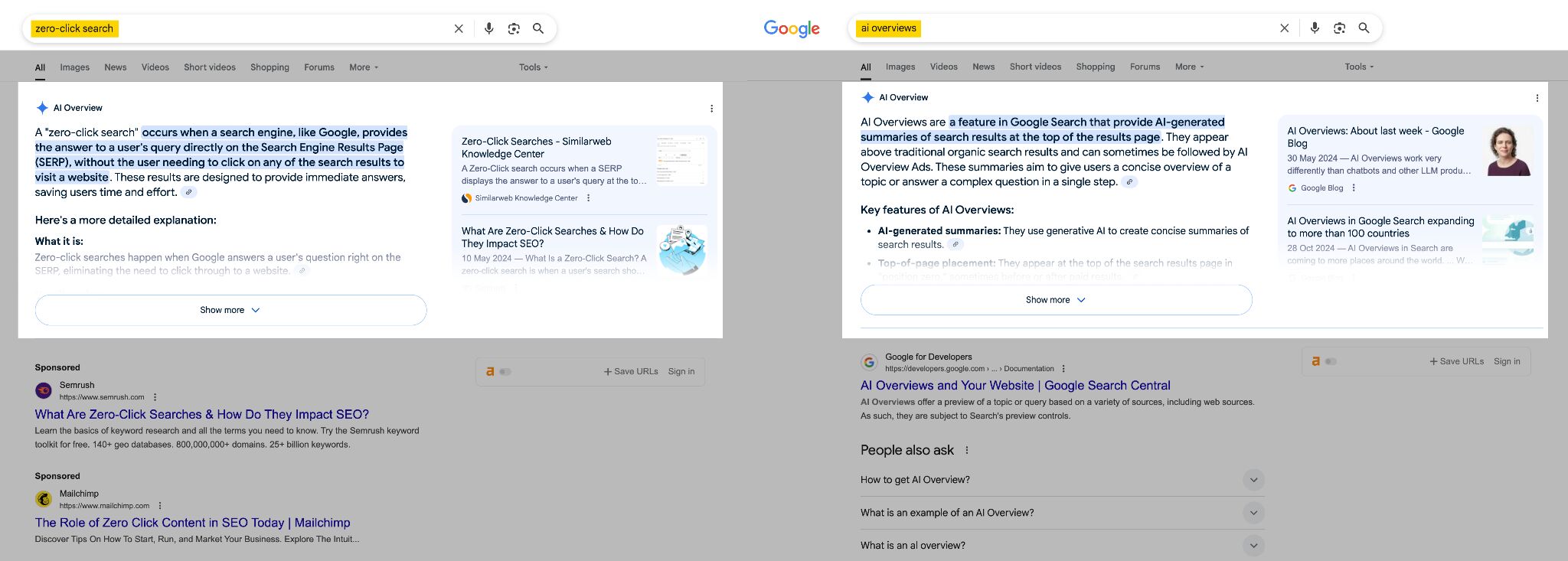
While AIOs do cite some webpages (linking to 7 URLs on average), the citation space is limited.
Many sources are hidden behind link icons or “show all” buttons, meaning users have to click once to find the source, and click again to actually reach the site.
AI Overviews do the opposite of incentivizing the click. If anything, they create a poorer UX for users who want to go deeper.
And there’s more in the way of citation problems.
Many AI Overviews will summarize content first, and cite second–meaning, they don’t always accurately match statements to the actual source–instead, they sort of wave a hand in the general direction.
In some situations, they conflate sources. They may, for instance, cite your competitor when recapping your content, sending them your (albeit dwindling) clicks.
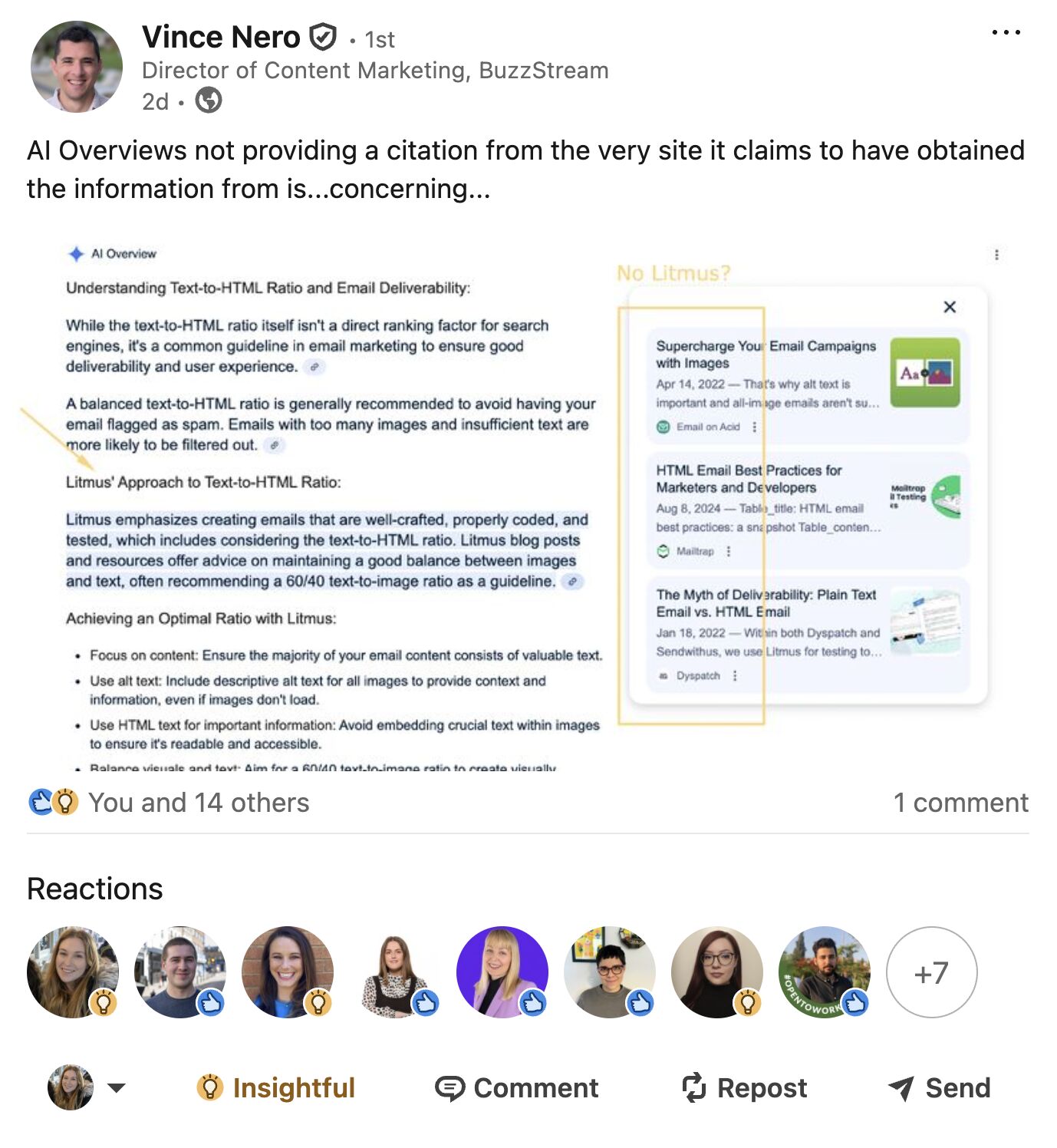
And in worst-case scenarios, they omit sources altogether.
For example, Vince Nero–Director of Content Marketing over at BuzzStream–recently noticed that AI Overviews recapped content from the email marketing platform, Litmus, but didn’t actually link to them.
AI Overviews are often recursive, creating zero-click search loops. In fact, nearly half of all AI Overviews point back to Google.
Google AI Overview appears with an underline, and when clicked, it redirects with a new query.@rustybrick @gaganghotra_ @brodieseo pic.twitter.com/Y6Df6bfxgn
— Sachin Patel (@SachuPatel53124) March 17, 2025
They can be problematic in other languages and countries too.
In a recent article, my colleague Erik Sarissky revealed that Google is now using AI and its AI Overviews feature to translate English-language content–and subsequently funneling users to its own proxy landing pages.
From there, it uses internal links to steer them to other Google-owned properties.
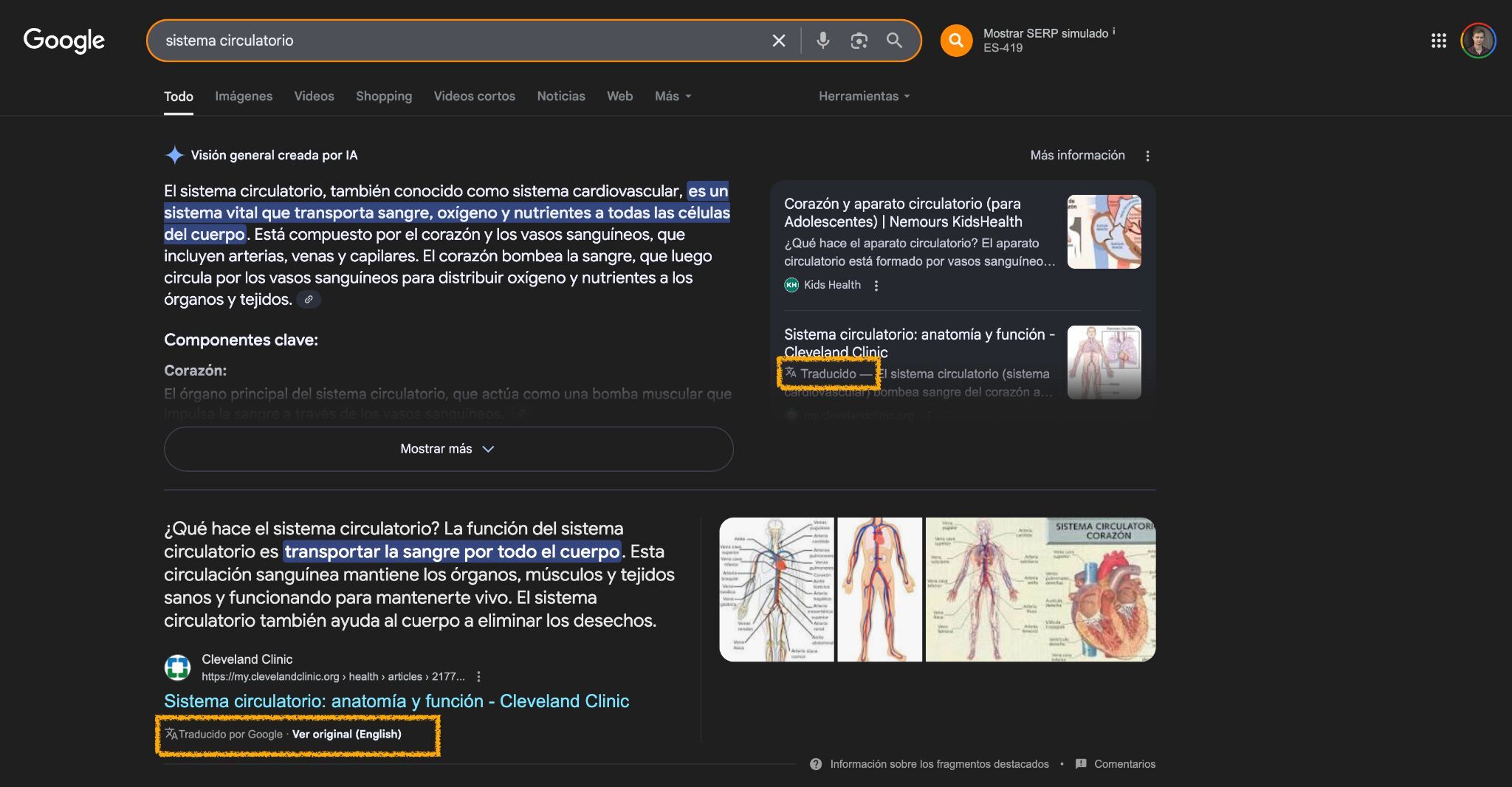
If users try to follow calls-to-action (CTAs) that lead to the original source, Google displays warning messages, discouraging them from leaving its universe.
This on Google translate domain
I translated to English using Circle to Search overlay
“For your safety .……” pic.twitter.com/RFxZbYBY79— Gagan Ghotra (@gaganghotra_) June 2, 2025
If you haven’t localized your content, you now run the risk of losing even more traffic to Google’s click-free SERP.
AI Mode
AI Mode is Google’s contextual, chat-based search mode.
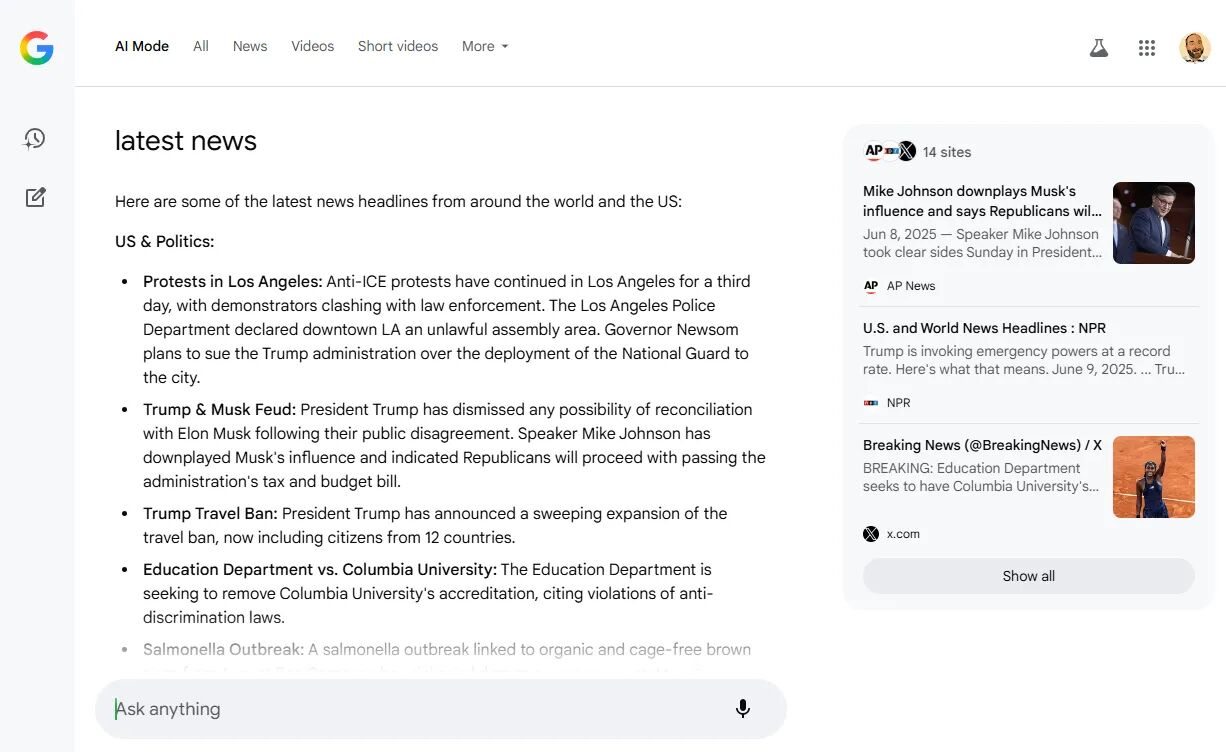
You can think of it like a stripped-back, search-focused version of Gemini or ChatGPT.
AI Mode has launched experimentally in the US, but as a tab alongside “News” and “Images”.
For that reason, uptake hasn’t been significant yet.
But Google has made its intentions clear. AI Mode will be slowly migrated to the main search page, until users become familiar with it.
At that point, it will become the primary search interface.
Featured snippets, local packs, search tools and more…
Google’s non-AI search results also display and summarize content from sites natively in the search results.
See below for some examples of SERP features that are most likely to reduce your clicks.
Ahrefs Keywords Explorer tracks the most prominent SERP features.
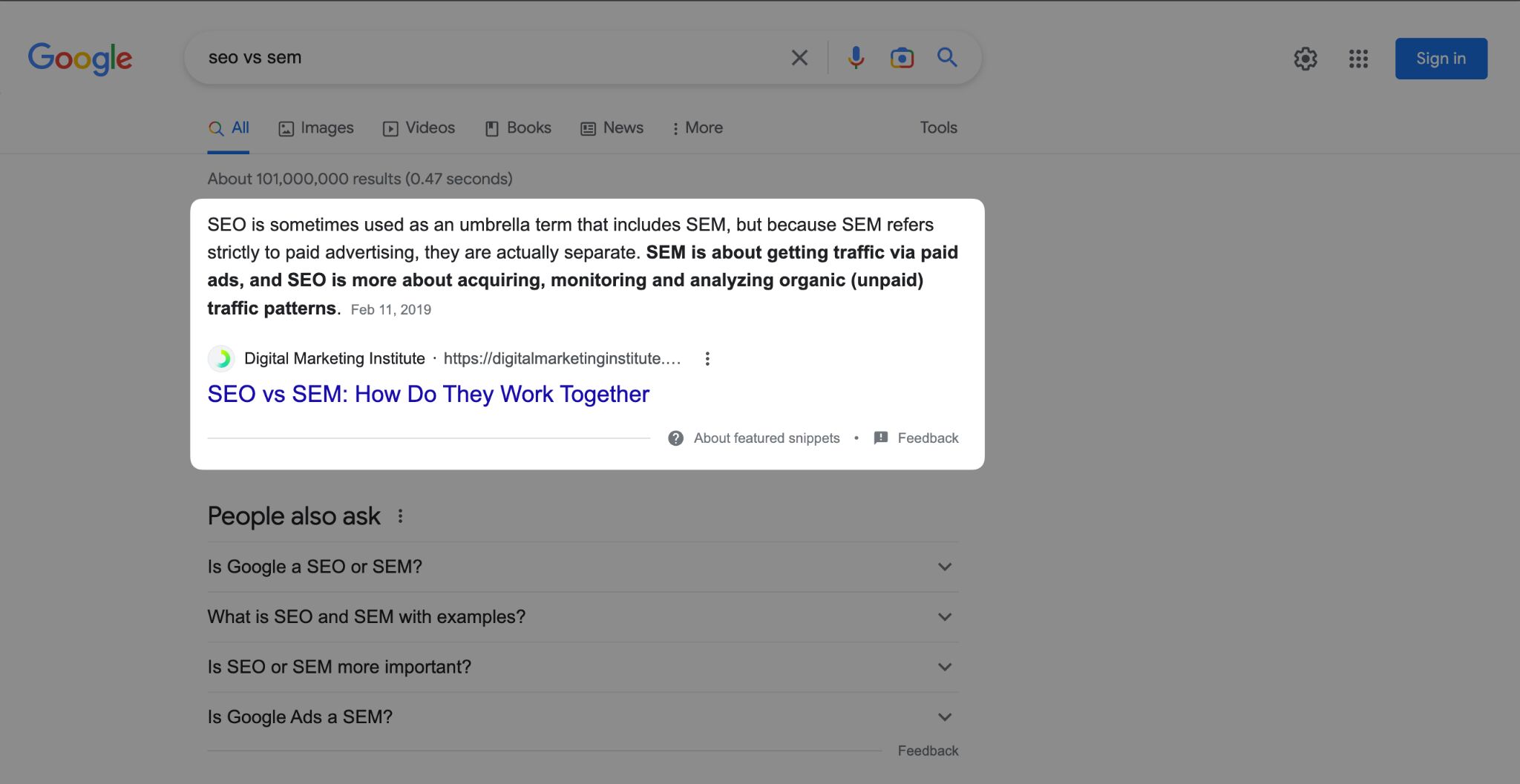
Featured snippets
Featured snippets scrape content from webpages, to surface instant answers at the top of the SERPs.
You can think of them as an early-stage version of an AI Overview.
But, unlike AIOs, featured snippets cite just a single website.
While they’re known to reduce clicks, they don’t present the same citation problems as AI Overviews–they lift exact-match content from a single site and clearly link to the webpage.
In some cases, featured snippets actually entice clicks rather than reduce them.
When the snippets don’t have enough space to answer the question in full, they end with ellipses or a “More items…” call-to-action.
Local pack
A local pack is a cluster of local business listings relevant to a user’s localized query, often leading to Google Maps or other native features.
Local packs typically include:
- Maps
- Opening times
- Directions
- Contact info
- Book a table CTAs park etc.
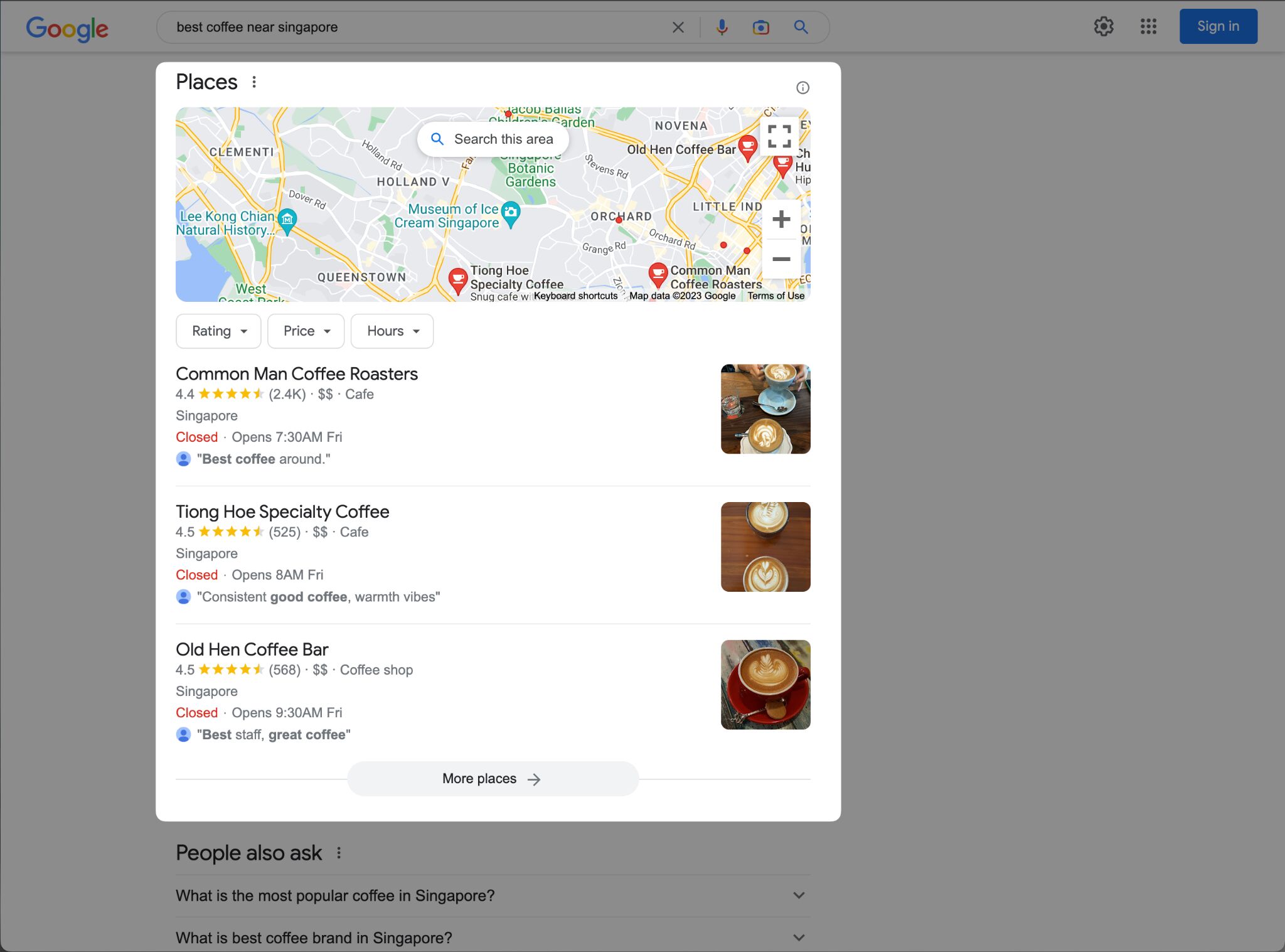
Image packs and thumbnails
Image packs are a row or block of image results directly featured in the SERP.
They provide a visual link to the Google Image tab, where users can go to view all their query-related images–without needing to click out of the SERP.
Knowledge cards and knowledge panels
Knowledge cards provide quick answers like facts, bios, stats, or definitions from structured data.
They can also include tools like:
- Calculators
- Clocks
- Weather
- Currency
- Translations
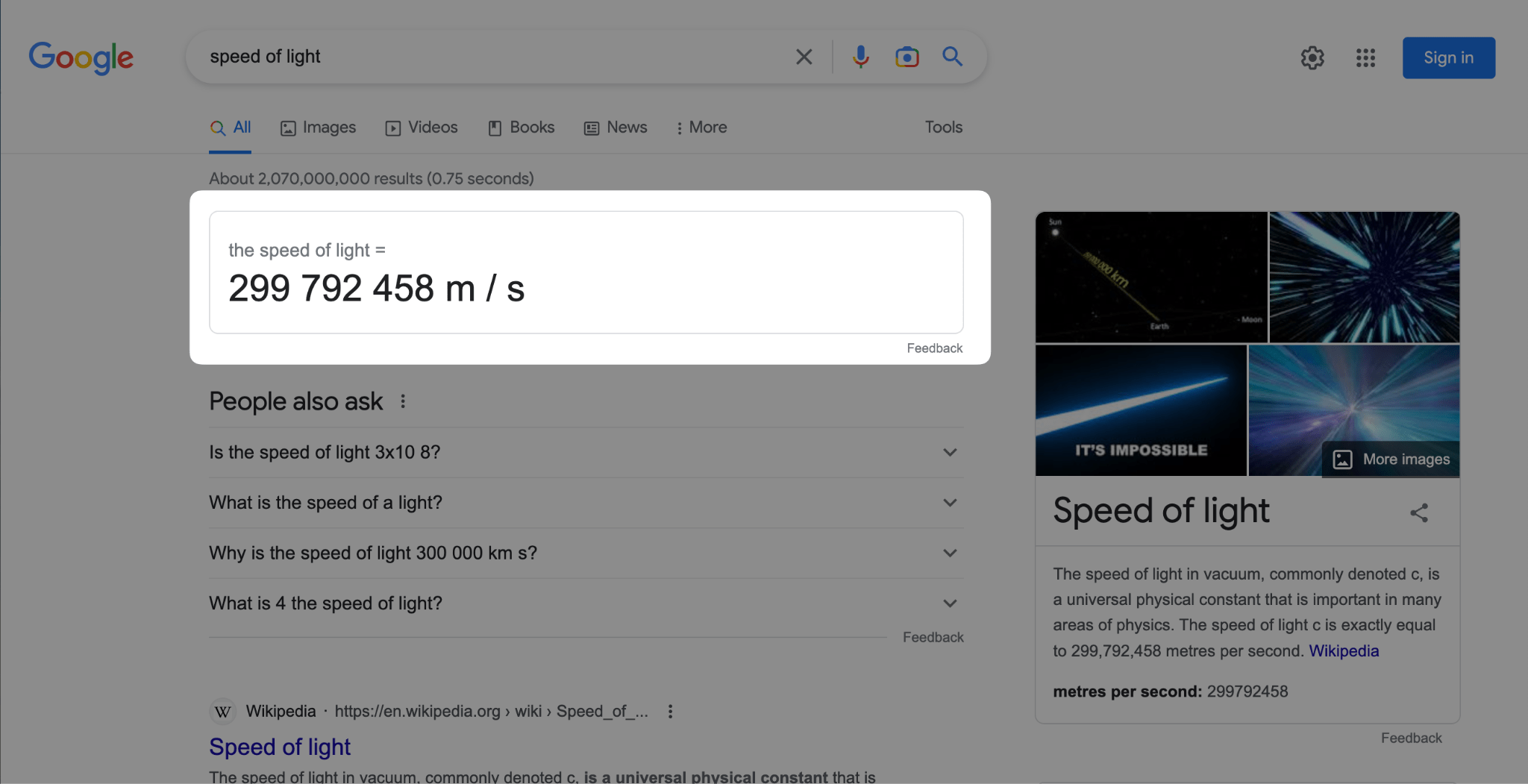
Knowledge panels give searchers top-level information about a topic on page one of Google.
They’re sourced from places like Wikipedia or Google’s Knowledge Graph, and are typically shown in a right-hand panel or card.
Further reading: What are SERP features?
Other Google-owned tools
Google’s own search tools are also cutting clicks to sites in certain industries.
For example, Google Flights and Google Careers curate flights and job listings for Google’s native ecosystem.
In some cases, users can complete flight bookings and submit one-click job applications without leaving Google’s walled garden.
And my research shows that Google is increasingly sending organic traffic to its own search tools.
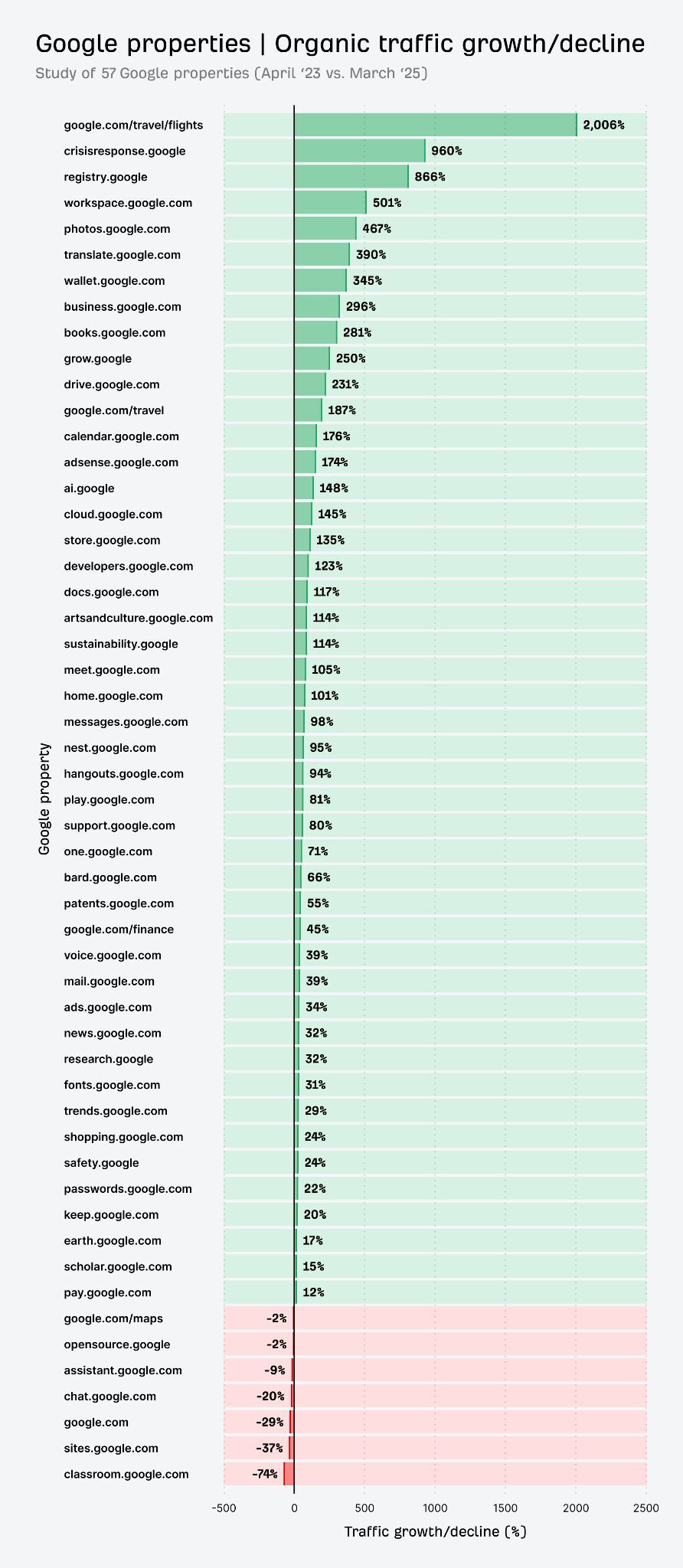
Zero-click search isn’t a temporary change or a puzzle to solve—it’s the new baseline.
Our job is to adapt.
Here are 7 things marketers are doing about zero-click search.
I think we can come clean and admit that we over-prioritized Google in our strategy.
When clicks were easy to come by, that worked a treat. Not so much anymore…
Now, we’re publishing with more intention, focusing on “Mutually valuable content”–content that supports our brand goals and offers real value to users.
Think: tools, templates, use cases, and workflows that are genuinely helpful, and deeply tied to the product.
At Ahrefs, this shift shows up in how we prioritize topics. We’re leaning into content that hits a sweet spot: it’s useful for our audience and unavoidably tied to our product.
Internally, we call this Business Potential—a measure of how naturally Ahrefs fits into the topics our audience cares about.
If a topic can’t be discussed without mentioning Ahrefs, we know we’re in the right ballpark.
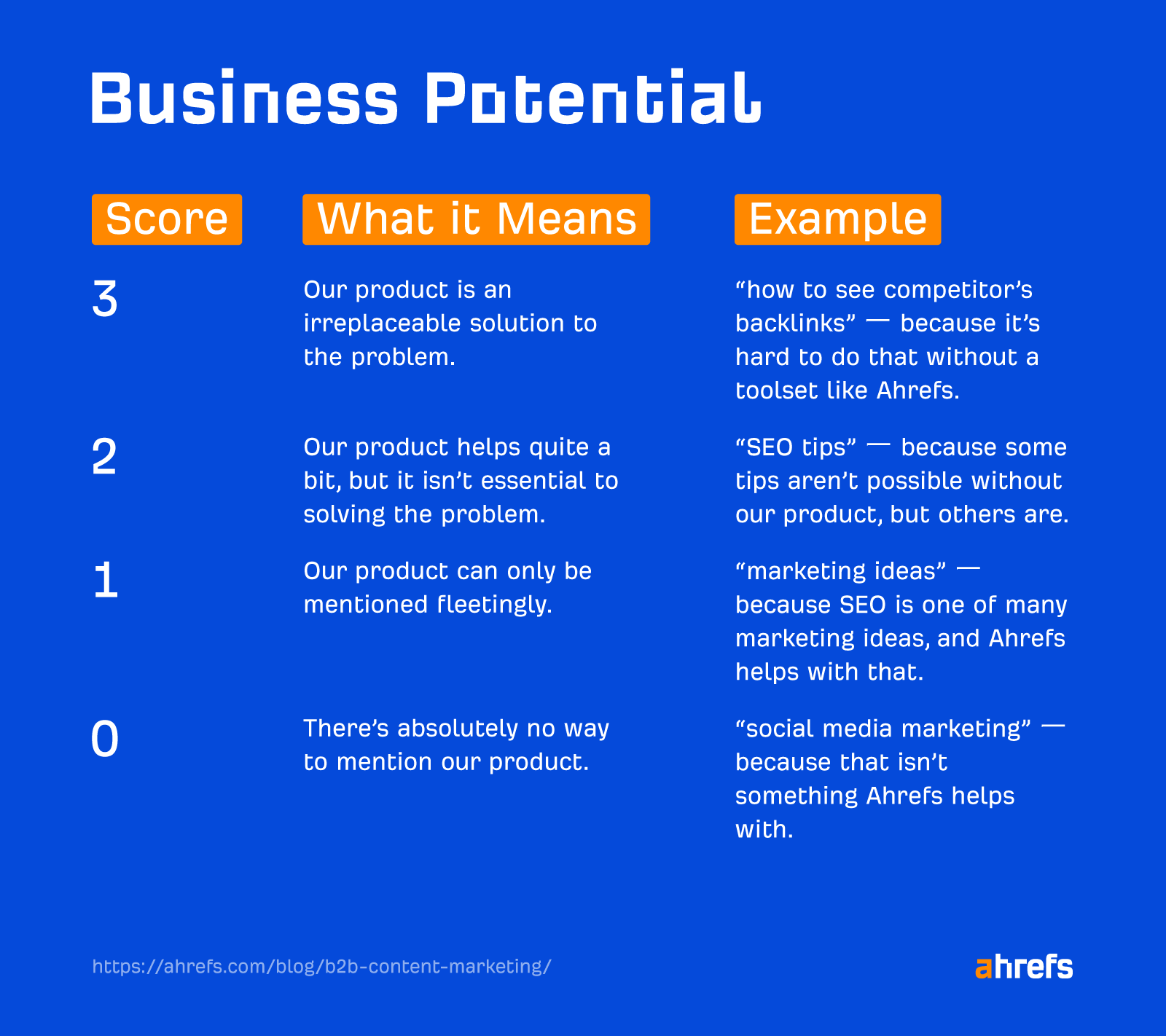
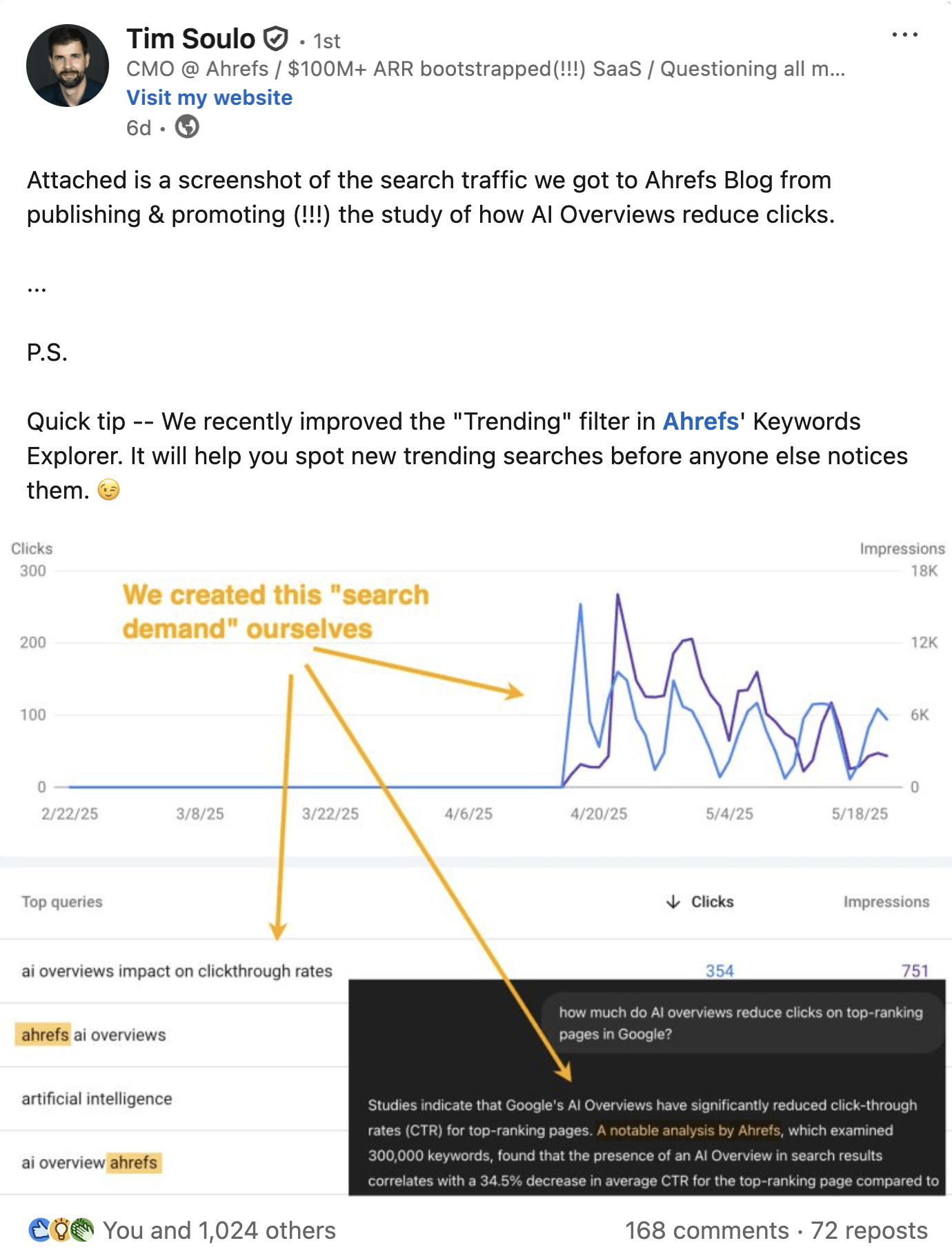
Case in point with our research into the click-loss spurred by AI Overviews.
We created the biggest (and first) study into the impact of zero-click search, and made sure our data and product were at the center of it.
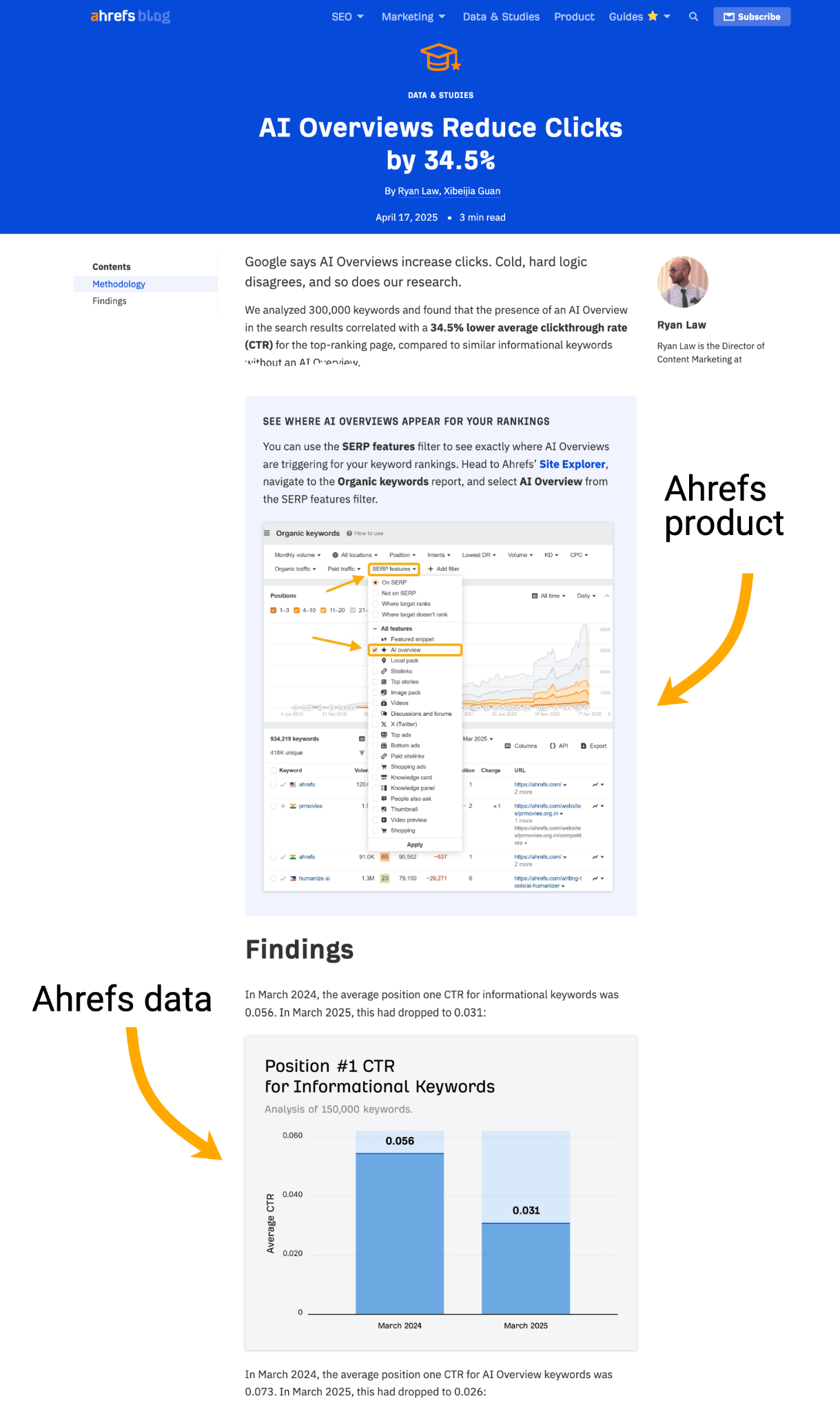
When marketers shared their own traffic drop-offs, they couldn’t help but cite our research–Ahrefs became part of the narrative.
And it worked pretty damn well–we drove tons of traffic from sources far beyond just Google.
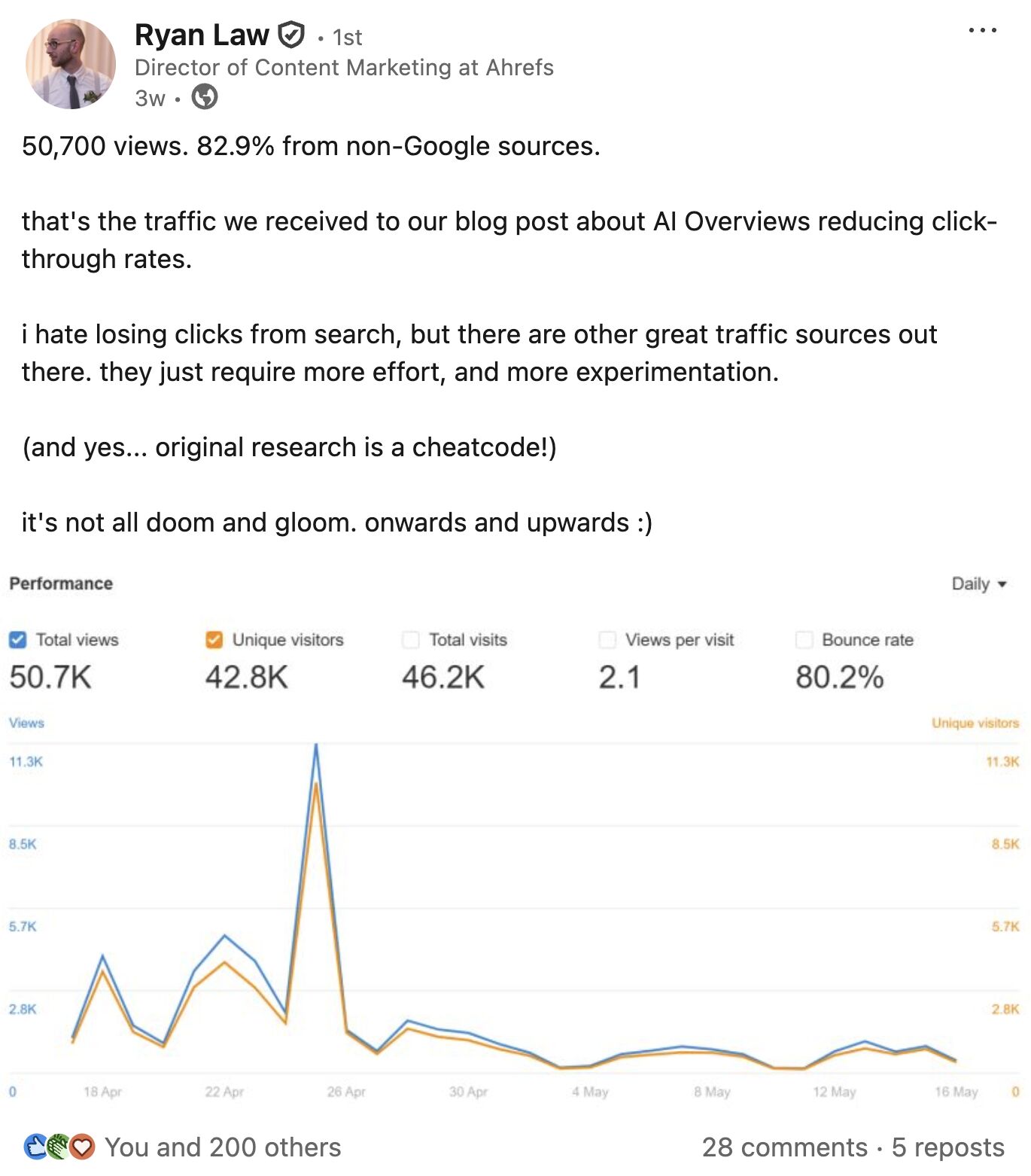
 Ultimately, marketers are shifting focus to build defensible IP—treating content as utility, not just traffic bait.
Ultimately, marketers are shifting focus to build defensible IP—treating content as utility, not just traffic bait.
After all, if it doesn’t drive clear conversions or user value, why keep feeding the machine?
We’re distancing ourselves from the AI-flattened “sea of sameness”, by developing content that:
- Validates our humanity
- Provides net-new information
This looks like thought leadership, opinion pieces, storytelling, data research, topic gaps, and gonzo content.
As AI content becomes ubiquitous, “humanity” becomes a serious competitive advantage.
We’re creating “deliberately human content” to draw a clear line between us and AI.
We want our marketing to say “hey, look, I’m human. You can trust me. I don’t give you broad strokes information, or hallucinated answers. I have lived experience. I will give you a trusted account and provide the receipts. I don’t parrot the same ideas over and over. I’ll tell you something completely new.”
Thought leadership, original research, and “gonzo content” centers real expertise, rather than rehashing the same known ideas, and generic information.
It’s the kind of content that makes a brand an innovator–not just a follower.
We’ve embraced this philosophy at Ahrefs, ramping up our creation of green-field research–publishing AI market share studies, AI marketing surveys, branded search traffic studies and more.
We also proactively hunt for topic gaps—ideas not yet covered by AI summaries and zero-click results.
Using Ahrefs AI Content Helper, we find underserved entities and target them to make sure we’re adding something new to the conversation.
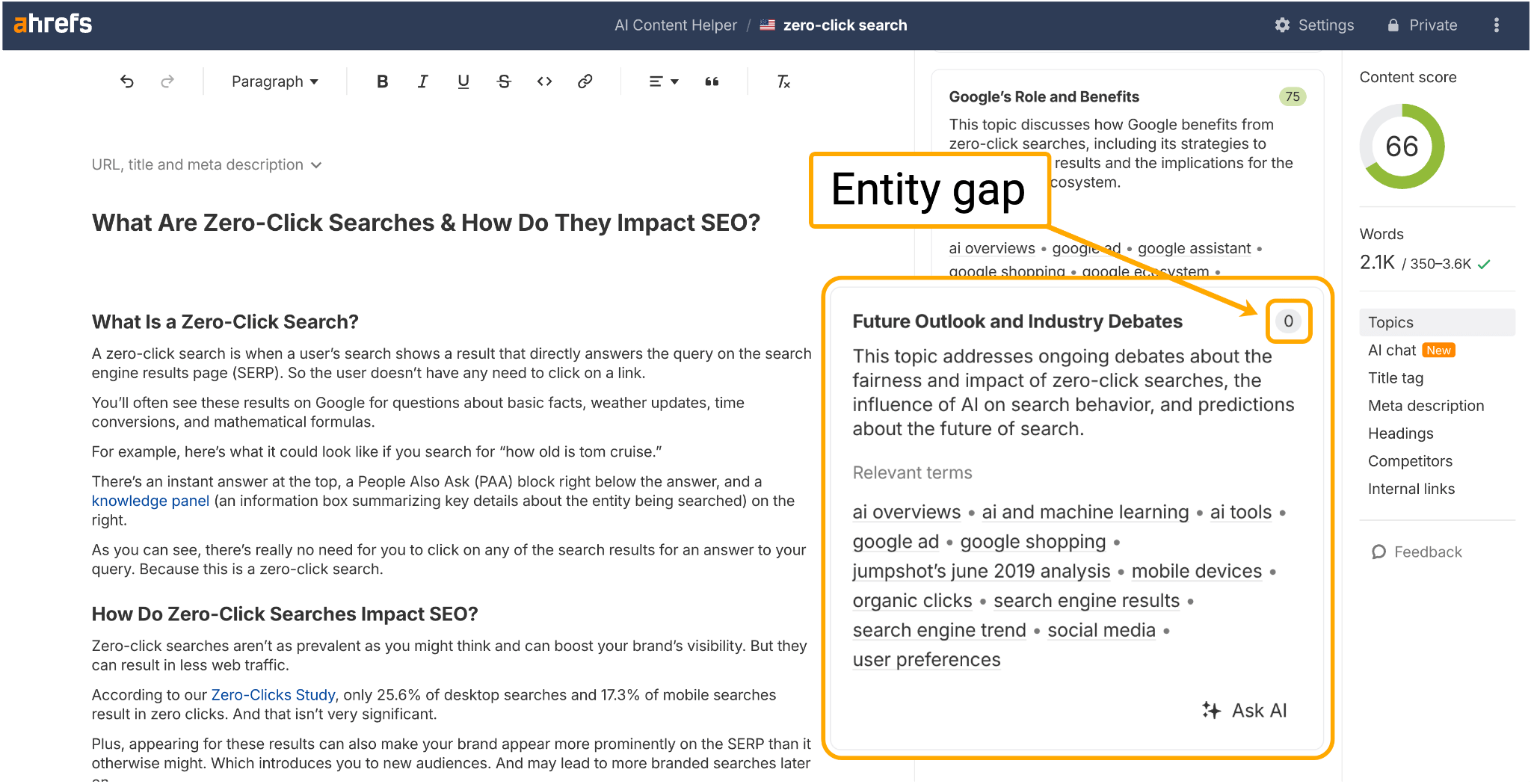
In fact, that’s why I’m writing this-here guide.
It seems there’s not enough in the way of “Future outlook” content into zero-click search right now.
Well, I am happy to oblige 😉
Searchers are asking more complex questions than ever.
No two queries are the same, and every user question is laden with intent.
That puts the pressure back on marketers to know their audience inside out. But it also means new opportunities for those who can meet that nuance.
While generic answers are the easiest clicks to steal, deep content is hard to summarize and even harder to co-opt.
For those reasons–and many more–we are getting granular with our content, and going “method” with our customer research.
“Going method” means that we’re tapping into long-tail questions, community threads, customer feedback, support logs, and site search queries–all to better understand what consumers really care about.

Gary Magnone, Managing Director at Magneti, advises The SEO Community to double-down on customer research and build out solid ideal customer profiles (ICPs)
And we’re providing the kind of answers AI can’t spitball or scrape from the SERP.
The more specific our marketing, the more niche problems we solve, the more likely we are to survive the click cull and find our “tribe”.
AI Mode is already personalizing results based on context and memory: including a user’s prior queries, location, and account behavior.
Meaning that when you master audience personalization, and make it into your customer’s world, you tend to stick around…
Here’s a framework you can borrow for nuanced customer research.
It involves mining the kinds of questions a user might ask when they’re wanting more than just the broad-strokes information contained in a zero-click search.
When they’re in the market for advice, personal experience, tips, and recommendations.
To find these queries, I’ve been using Ahrefs and ChatGPT.
First up, I head to Ahrefs Content Gap tool where I set up a search that shows me where my competitors are visible–but I’m not.
I basically want to find all the complex questions my audience are asking that I haven’t yet answered.
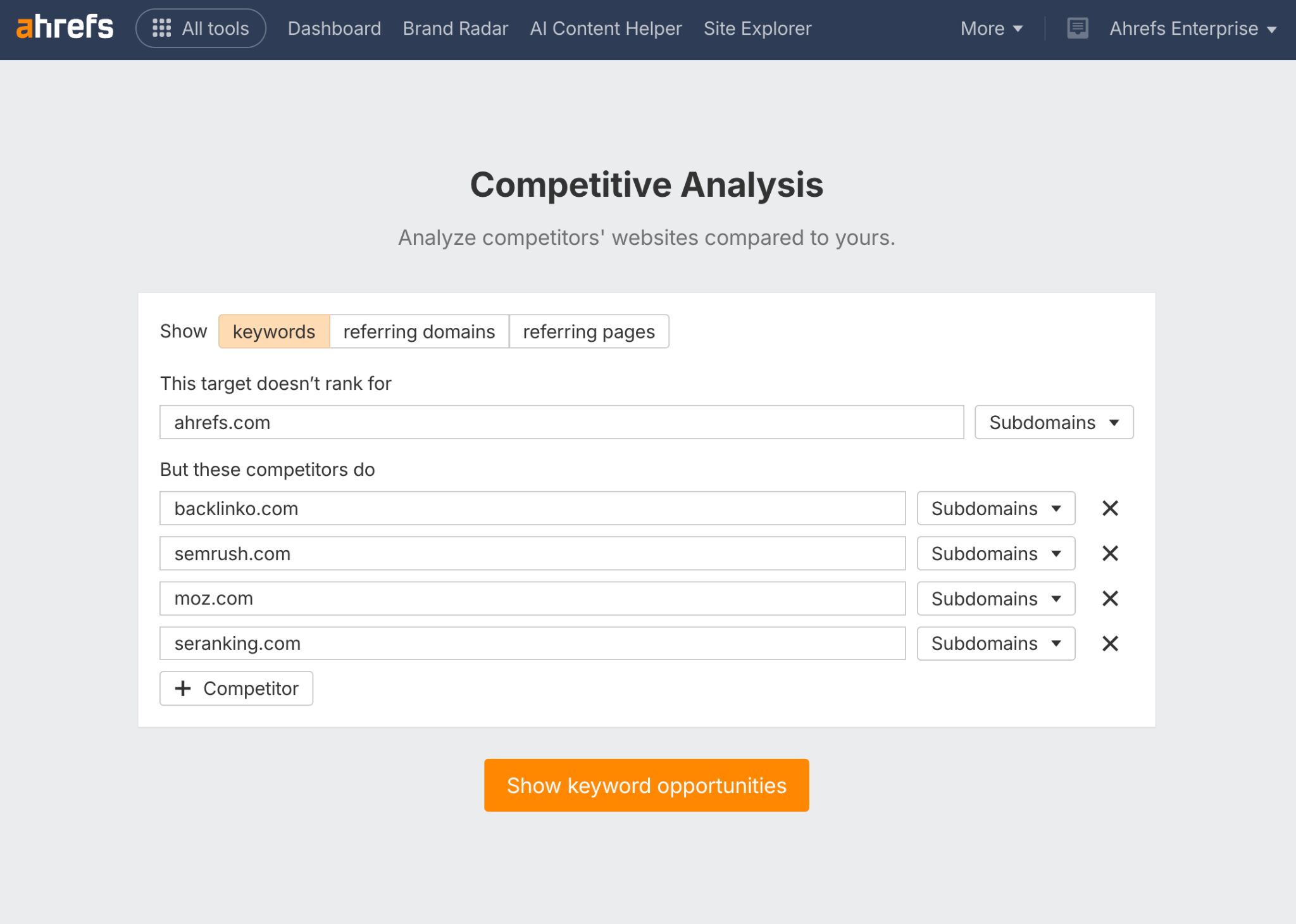
From there, I set up the following filters:
- A minimum word count of 6 words, so that I’m focusing on nuanced, long-tail phrases.
- A keyword starts with: “how” filter. Of all the question-based keyword modifiers, “how” is the one most likely to suggest there is a complex job-to-be-done.
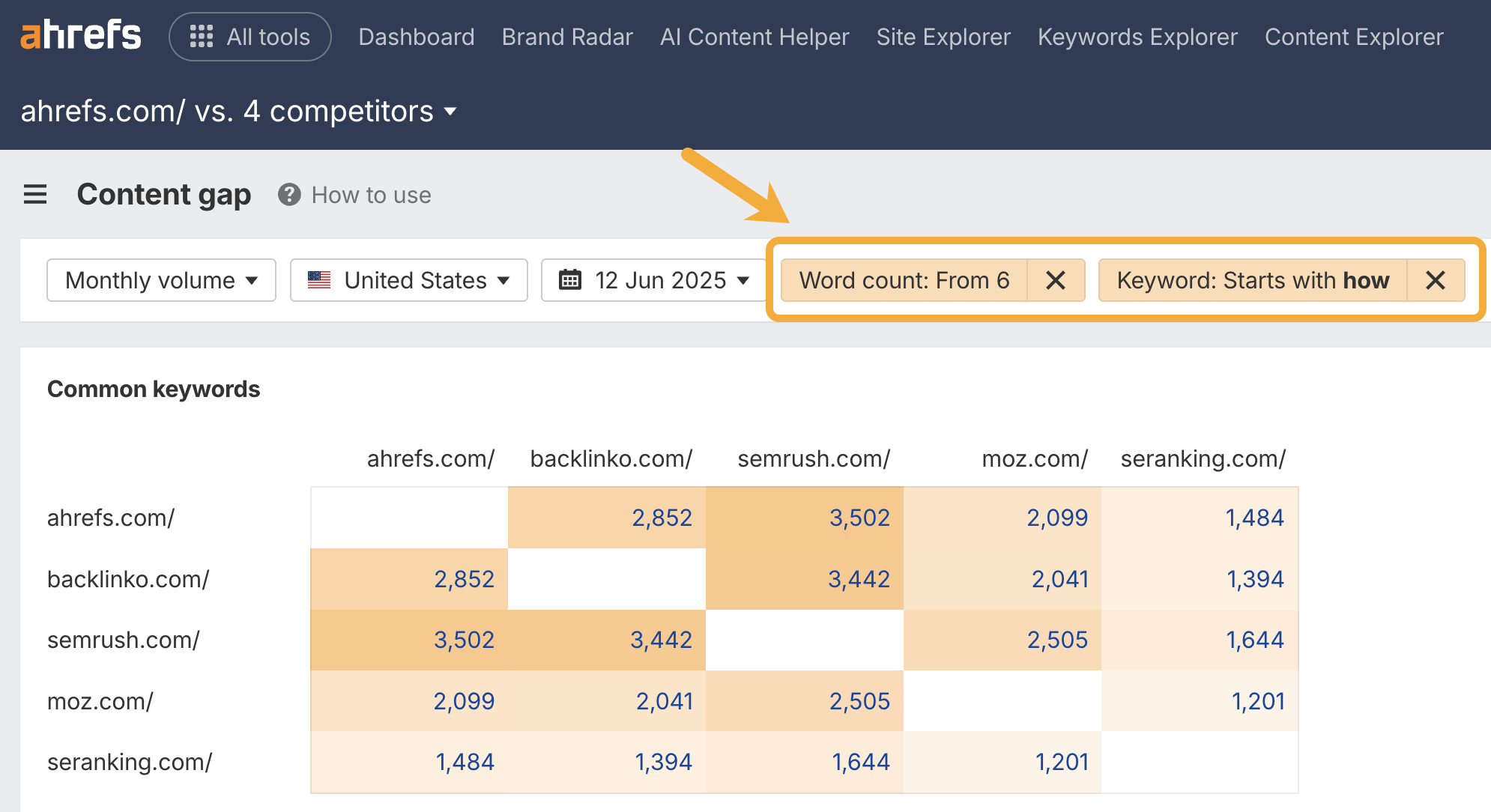
Then I make sure:
- I’m not ranking
- At least two of my competitors are ranking (in the top 100)
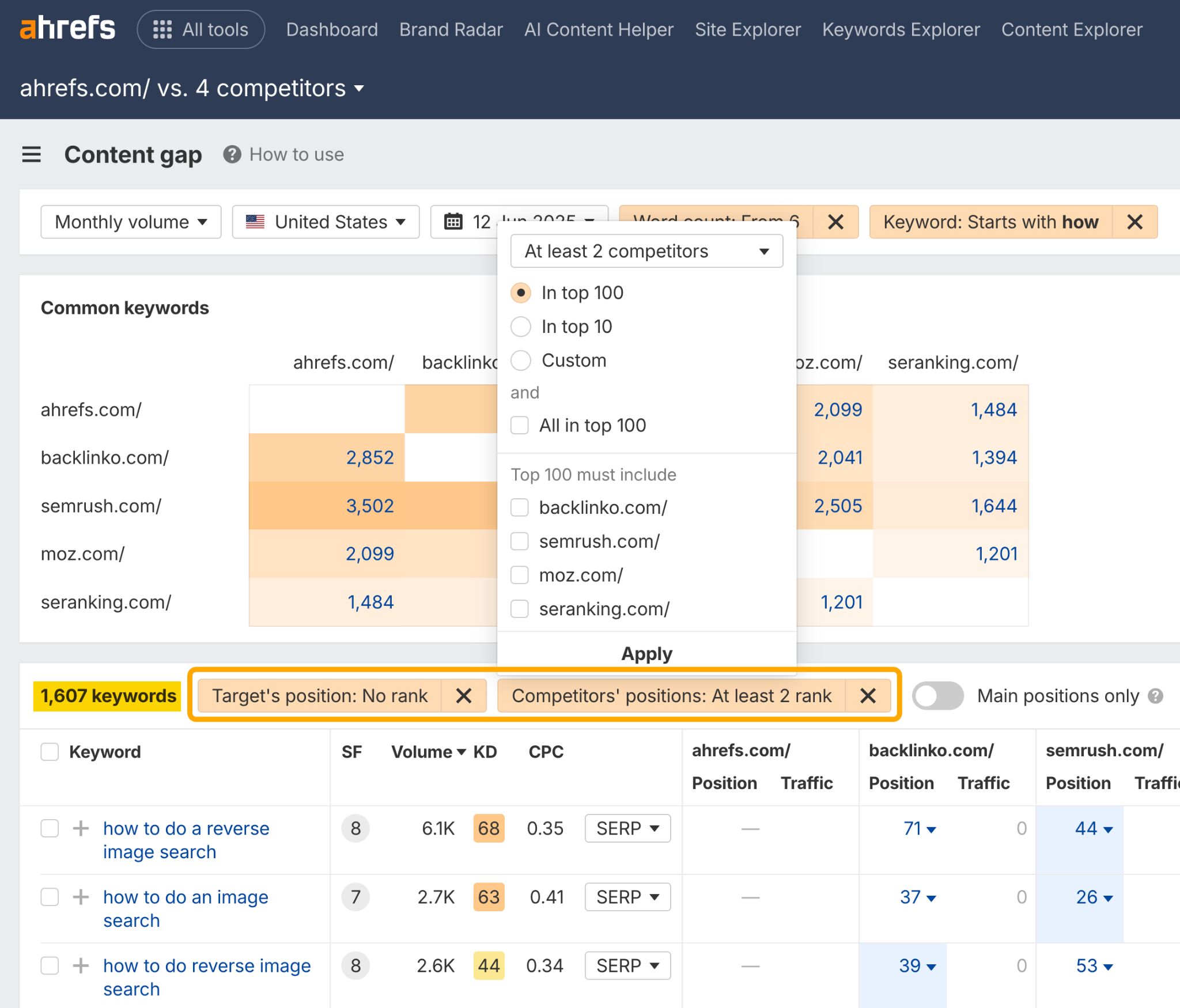
From there, I export the returning 1,607 keywords, and head to ChatGPT, where I drop the following prompt into the o4-mini model (best for advanced reasoning tasks):
Please score the keywords on this list according to the following scale (1 = a broad, vague question that can be answered easily and succinctly, 10 = a nuanced, hyper-specific question that can’t be answered easily or succinctly)
I attach my csv. export of keywords which I’ve cleaned to include just the keyword and volume columns.
When ChatGPT’s done scoring, I’m left with a list of complex user questions.
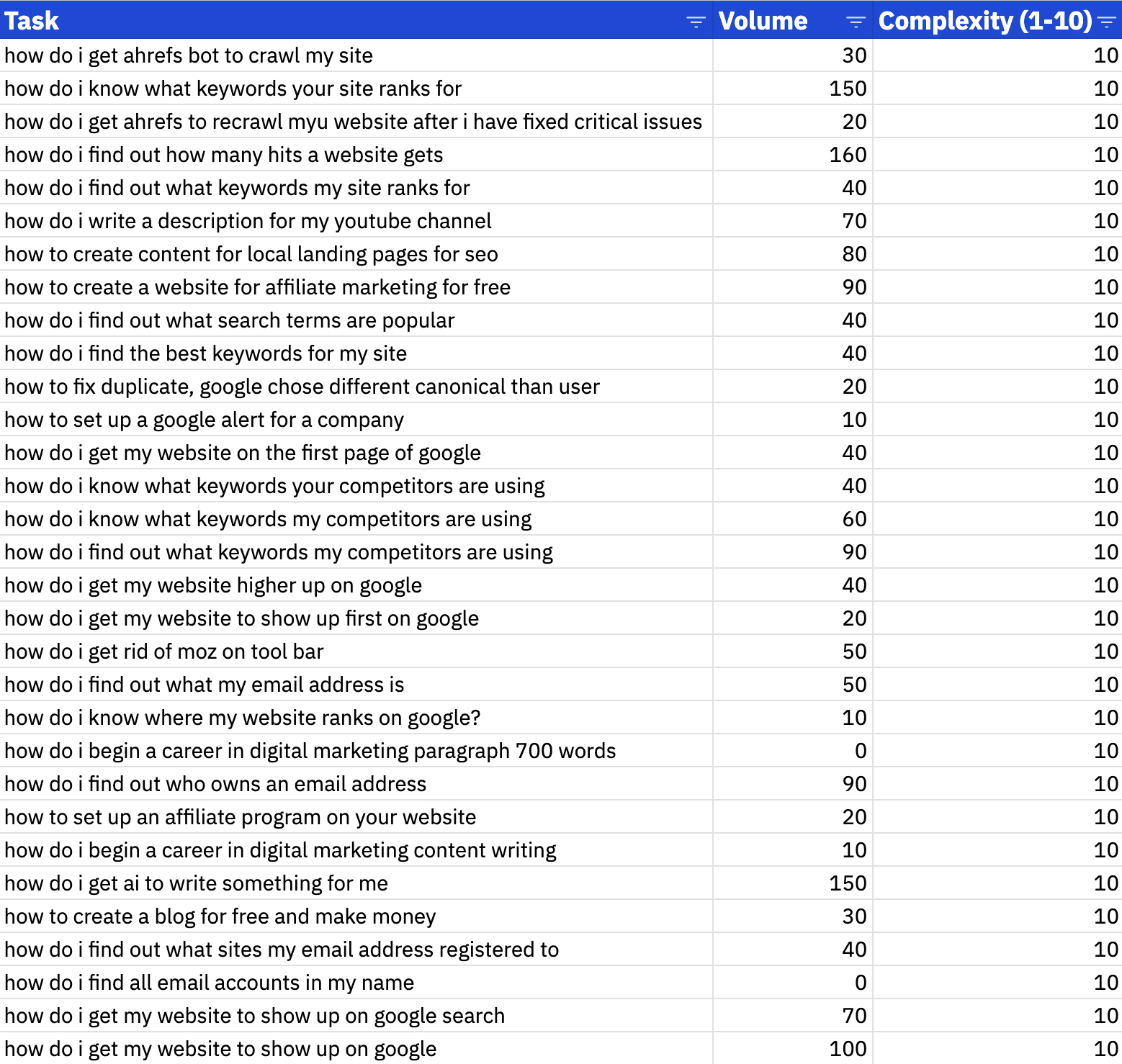
To prioritize this list, I can filter to zero-in on questions with a complexity score of 9s or 10s, and then sort by descending keyword “volume”.
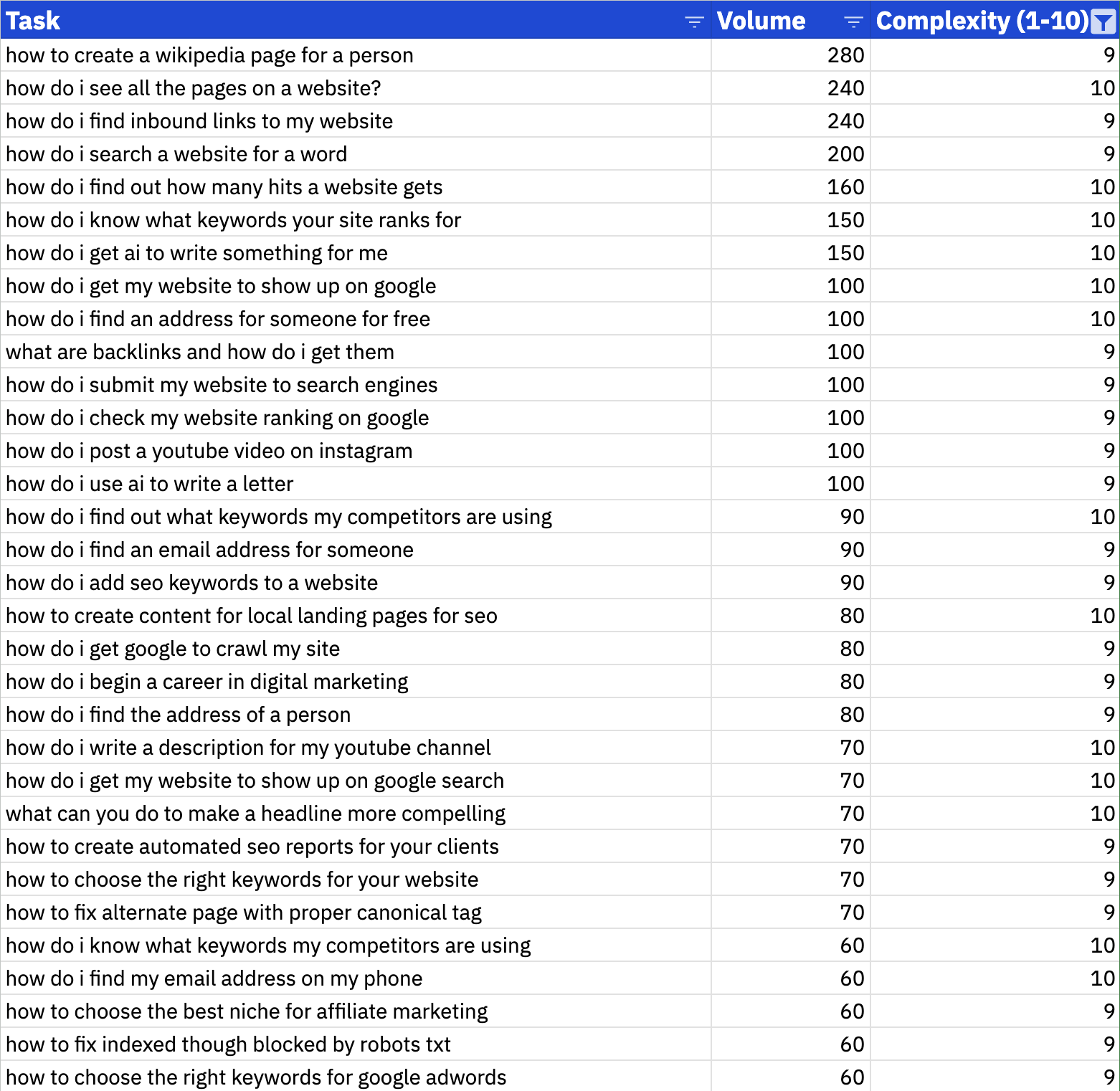
From there, I’ll make a final judgement call on “Business Potential”, based on how relevant the question is to Ahrefs.
In a zero-click world, depth beats breadth. And depth starts with customer research.
Now that search is sans click, traffic diversification is the #1 thing on everyone’s mind.
Google used to be the destination. Now it’s just one of many.
PR, TikTok, Reddit, Substack, Slack, WhatsApp—anywhere people talk, decide, and discover is where we now want to be.
The smartest SEOs are making sure they’re not stuck in search.
They’re diversifying their channel mix, and building their business on land they own–not search real estate they rent.
The message is clear. Publishers need to focus on audience strategies that exclude Google as a reliable source. The emphasis needs to be on non-Google channels, multimedia content, and direct brand traffic.”
A byproduct of this: we’re collectively remembering just how important content promotion is.
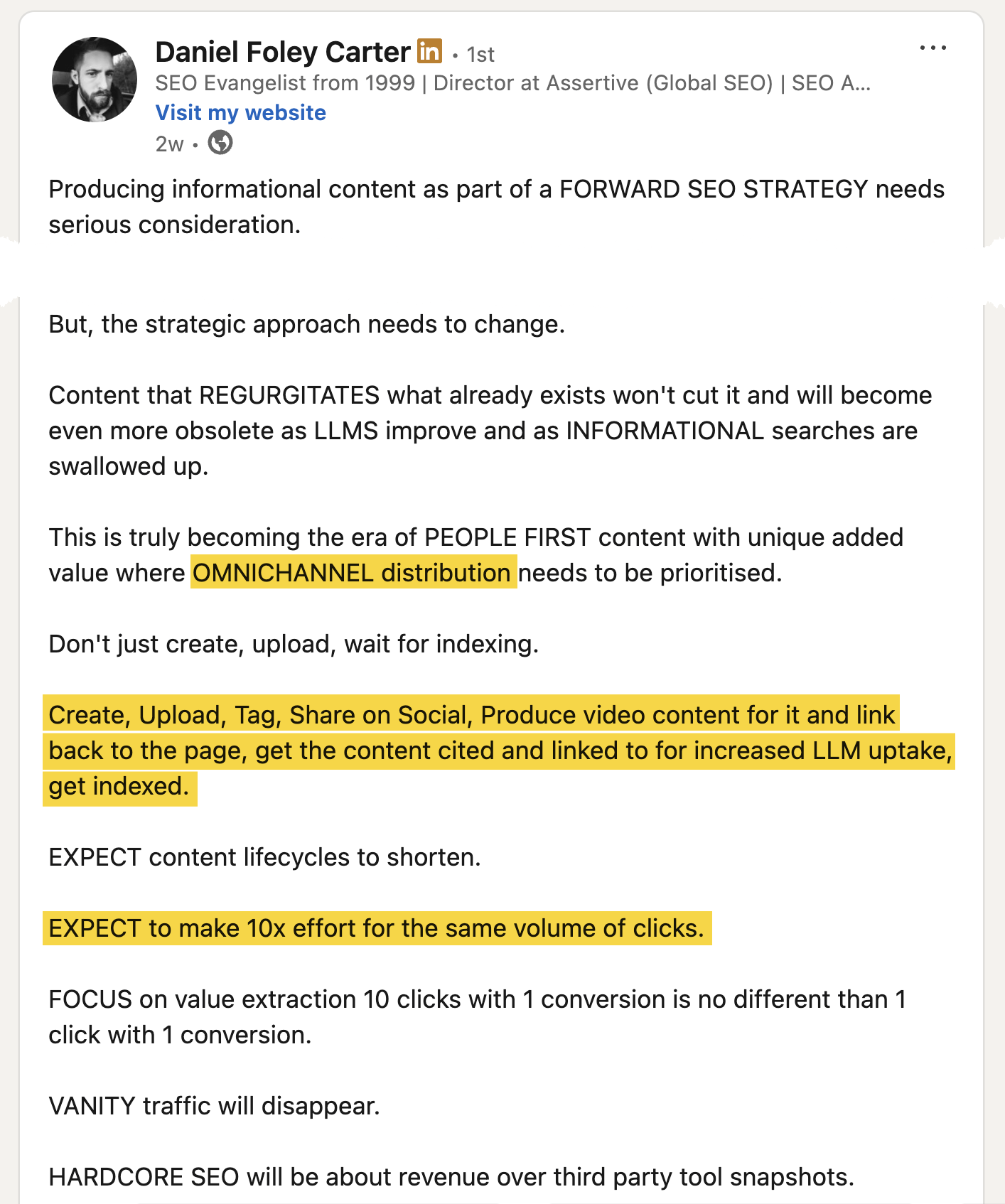
The future of informational content is demand-led and you’ve got to start thinking of how you can drive demand with informational content, not just educate.
Gone are the days where we could work through a laundry list of SEO ranking factors, and build a nice, steady stream of traffic.
We’re having to start operating like marketers again.
As my colleague Despina rightly says, “Good SEO plus lazy marketing won’t cut it anymore.”
SEO delivered outsized returns for so long, while social, PR, email and other business functions had to put double reps in for half the gains.
Now the time has come for us to make 10X the effort for the same volume of traffic that once came so easy.
So, we’re moving towards something like what Rand Fishkin calls “Search everywhere optimization”.
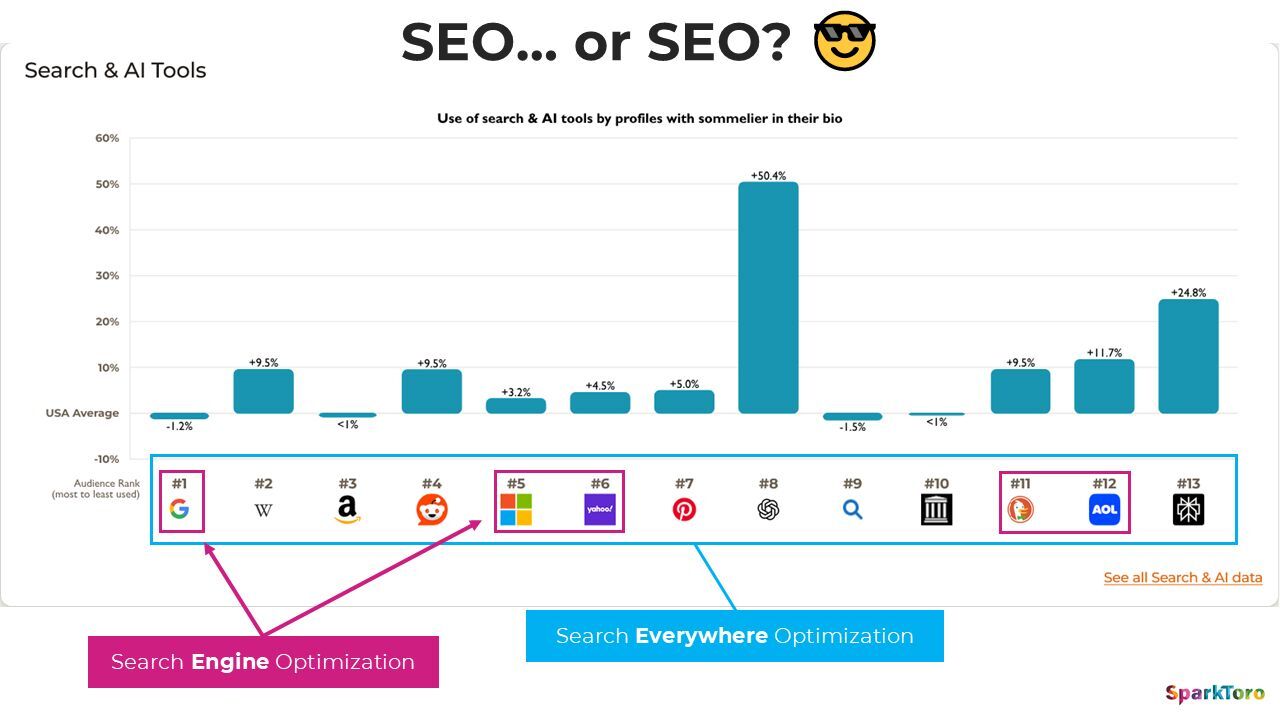
We’re having to:
- Distribute ideas, not content: According to Ahrefs’ CMO Tim Soulo, we need to promote our most disruptive ideas natively on each platform–not clicks to our site.
- Own the demand: Google never actually created the demand–63% of the traffic Google sends is navigational (SparkToro), and 46% is branded (Ahrefs). We just need to take back ownership. Chima Mmeje advises creating content experiences that give people a reason to return to your blog/site again and again.
- Change our benchmarks: We need to monitor mentions, shareability, referrals, and sentiment–not just traffic.
For us, LinkedIn is working pretty damn hard as a source of referral traffic, and ChatGPT is majorly picking up the slack as our organic traffic takes a hit.
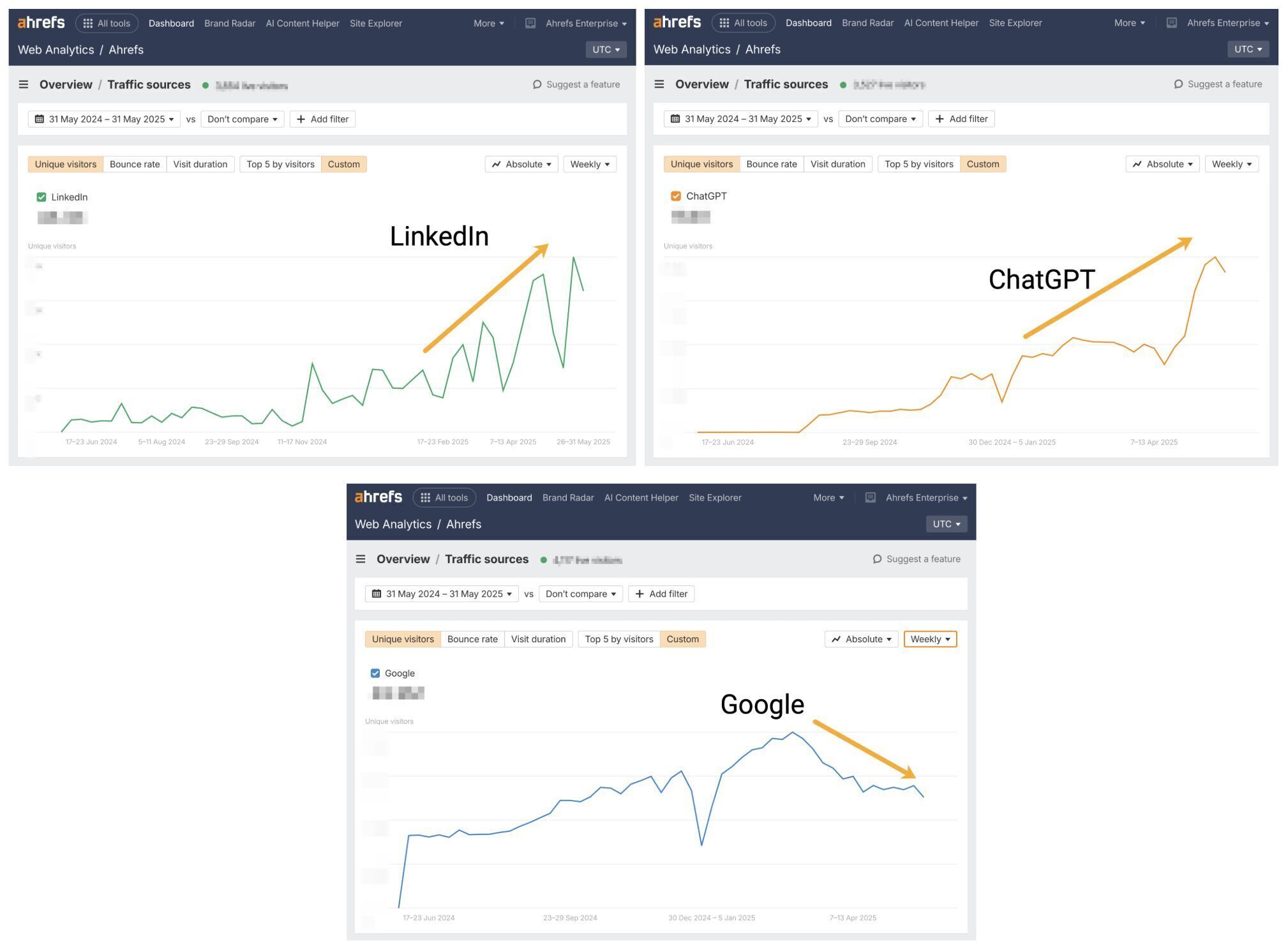
Look deeper into your own analytics data, and see which channels you can zhuzh to drive audiences to your content.
This next part isn’t about abandoning SEO. It’s about making sure you’re not dependent on it.
The less visibility you get in the SERPs, the more you need people to already know who you are.
For that reason, we’re starting to invest more in off-site content.
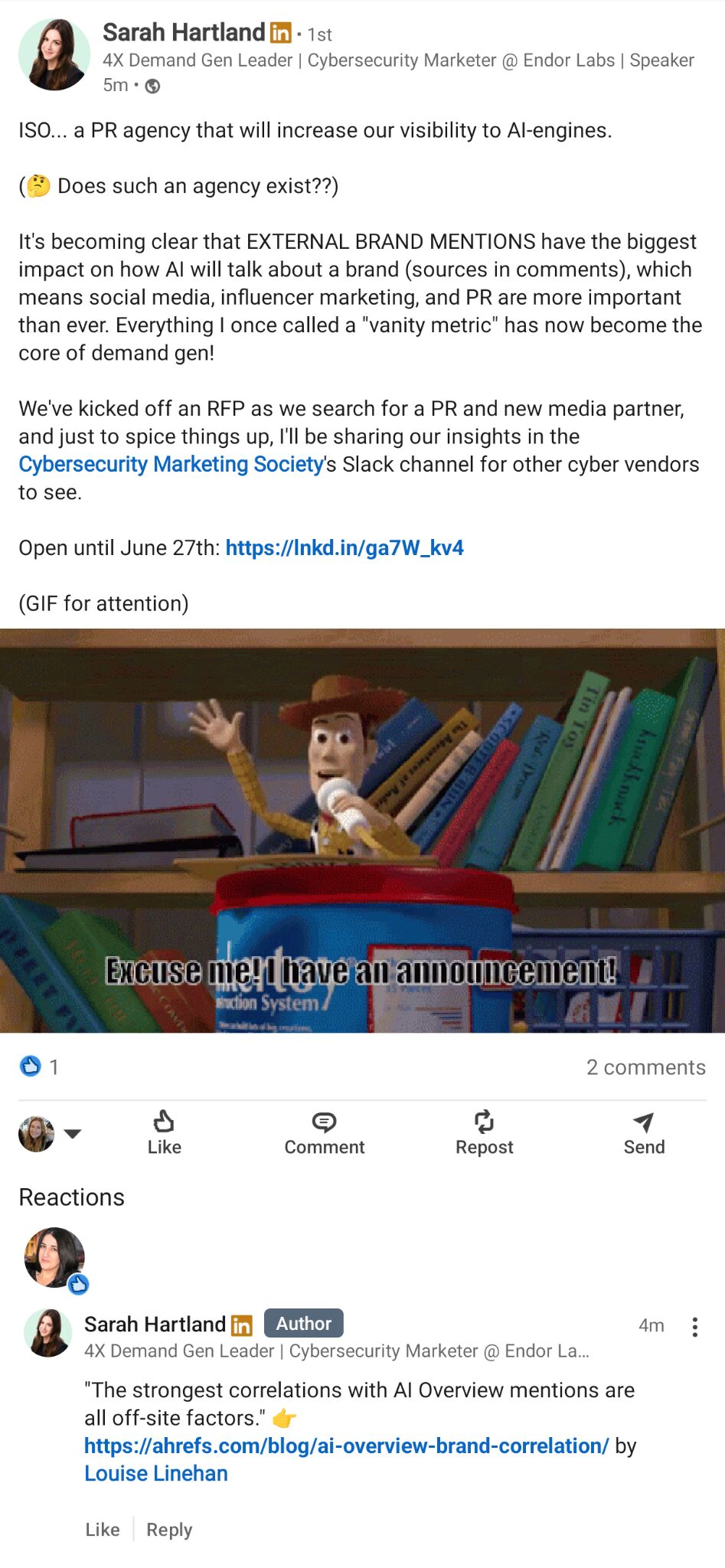
Sarah Hartland “In search of” a PR agency to increase visibility in AI by way of social media, influencer marketing, and PR
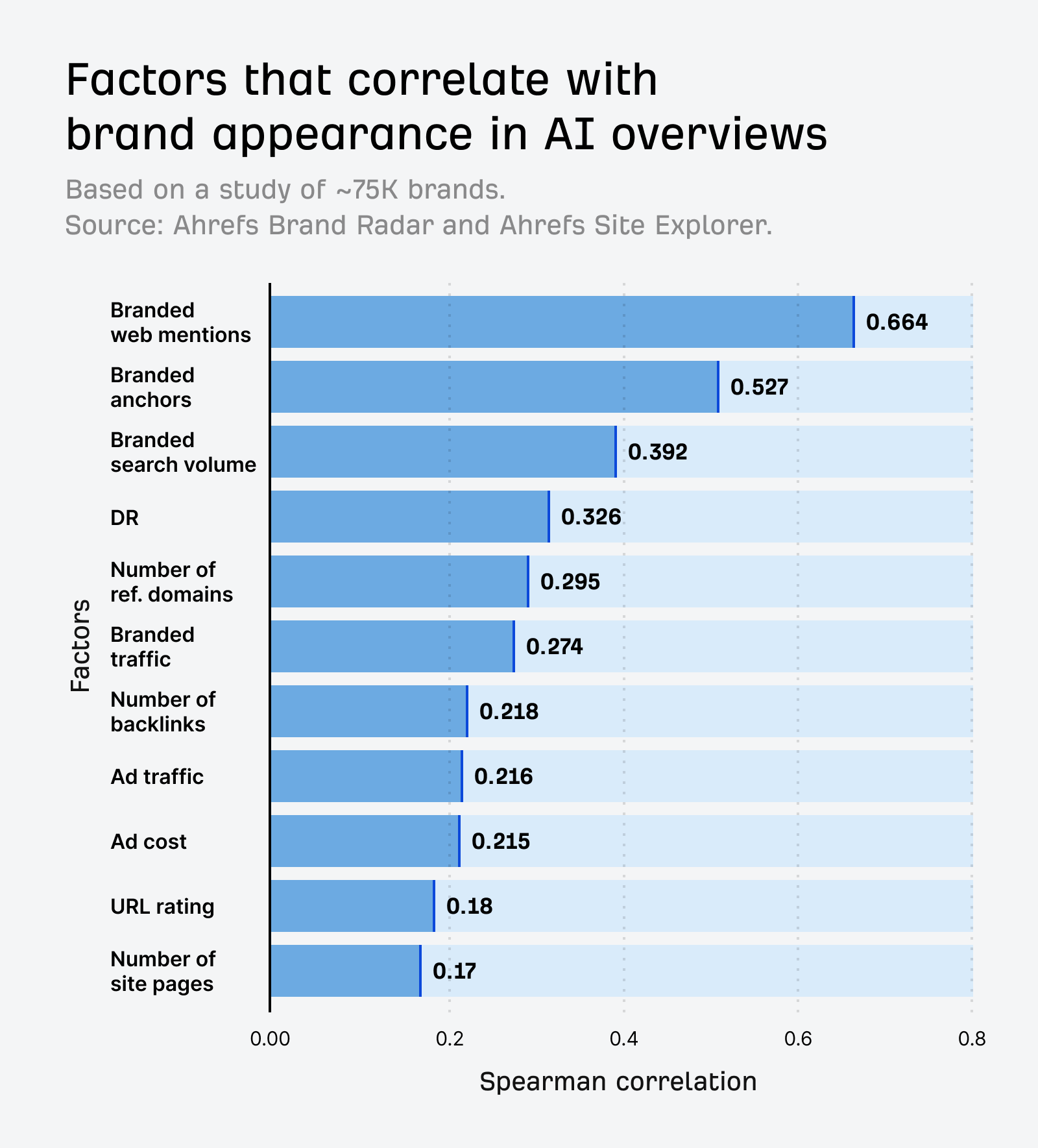
PR, earned media, and brand mentions pack the greatest punch when it comes to zero-click search and AI visibility.
This has been a long-held theory, but we’ve found proof in our study of 75,000 brands and the factors that correlate with brand mentions in AI Overviews.
But the takeaway for marketers here is not: build branded web mentions with a bit of “lite” PR.
And it’s certainly not paying for mentions, guest posting, or off-site “entity engineering”.
In other words, it’s not about feigning brand reach.
It’s about building a brand that gets mentioned.
The mentions are the byproduct of strong brand affinity.
And we’ll have to work our socks off to build that brand.
Through strategies like PR, yes, but also through:
- Search everywhere optimization: Showing up on every platform their customer touches.
- Building an incredible product experience: Providing exceptional customer support, deep documentation, and “surprise + delight” features that get people talking. Promoting open-source tools for “post-click” search, creating live feedback loops, and “building in public”.
- Fuelling public discourse: Encouraging reviews on platforms like G2, and the sharing of use cases, workflows, and discussions on Reddit. Ultimately, showing up in customer communities.
- Launching “noisy” narrative-driven campaigns: Investing in creative stunts, branded content, data-storytelling, and inventive product launches (not just announcement blog posts) that are made to be shared, and appeal to audiences on more of an emotional level.
- Engineering “Word of mouth” marketing: Coining original theories, frameworks, or important brand topics, then taking them “on tour”, and engineering the ways in which audiences talk and think about the brand. Here’s Nathan Barry (founder of Kit, formerly ConvertKit) talking to Tim Soulo on the Ahrefs Podcast about how marketers should be “equipping customers with the ability to tell the story of their brand.”
Google’s latest guidance reads like déjà vu: make great content, use structured data, mix up formats.
What’s changed is the goalpost—it’s no longer about ranking. It’s about “earning a place in AI answers.” In other words: zero-click visibility.
What Google’s guidance fails to mention is the monumental collapse in traffic and attribution that comes with that.
For many, the exchange feels broken.
We’re seeing a few early forms of pushback.
Some marketers are disabling AI search…
More and more are blocking AI crawlers…
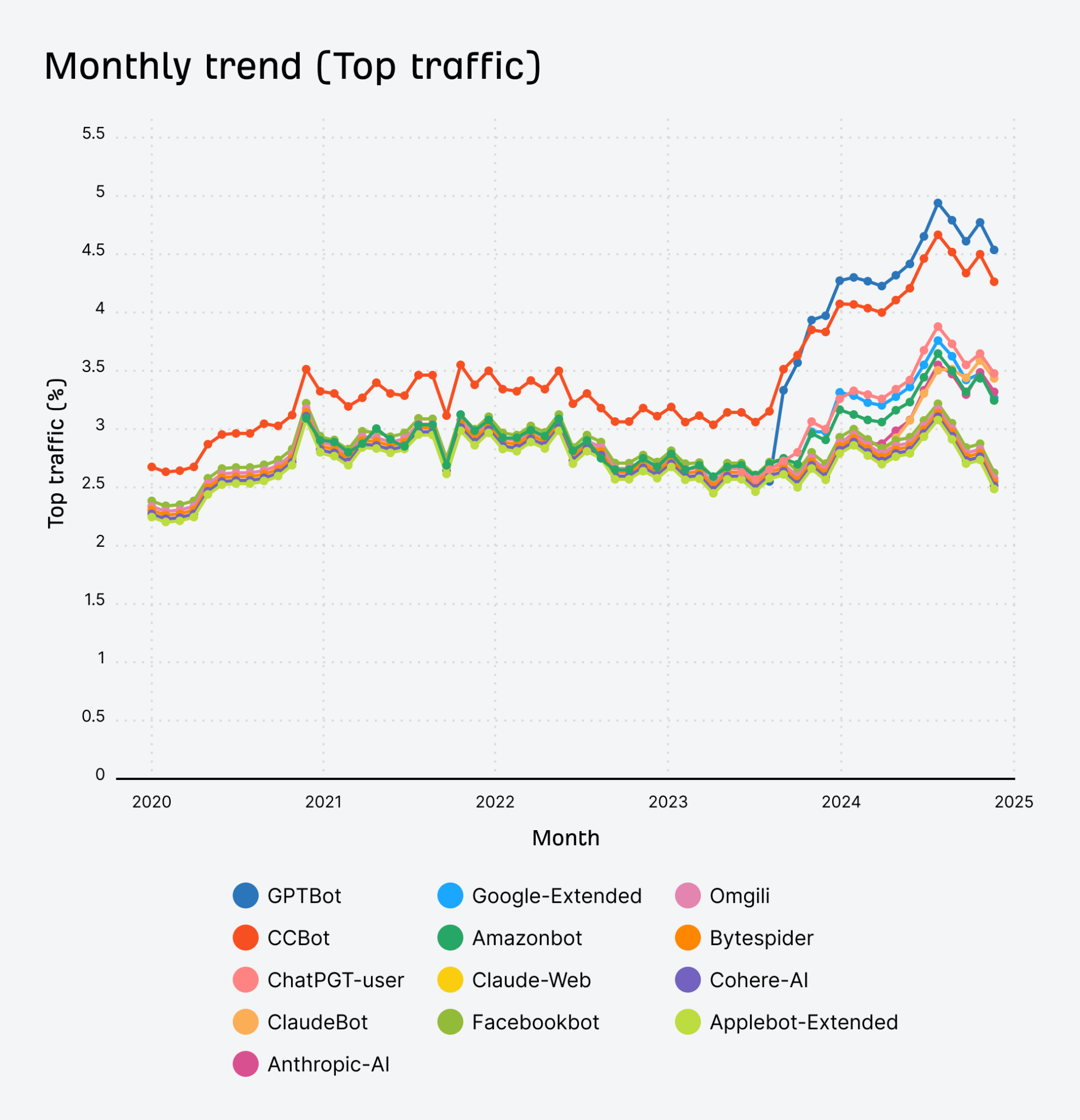
Top-trafficked sites began blocking AI bots in 2024
Some are refocusing on non-search channels…
Some are even taking legal action to push back on their content being mined for training data ¹ ².
Google’s zero-click search has certainly shaken things up.
Google’s zero-click search features are reducing our traffic, but by how much?
That’s the million-dollar question.
Marketers are desperate to track zero-click data, to understand its full impact on traffic.
But Google’s not making it easy.
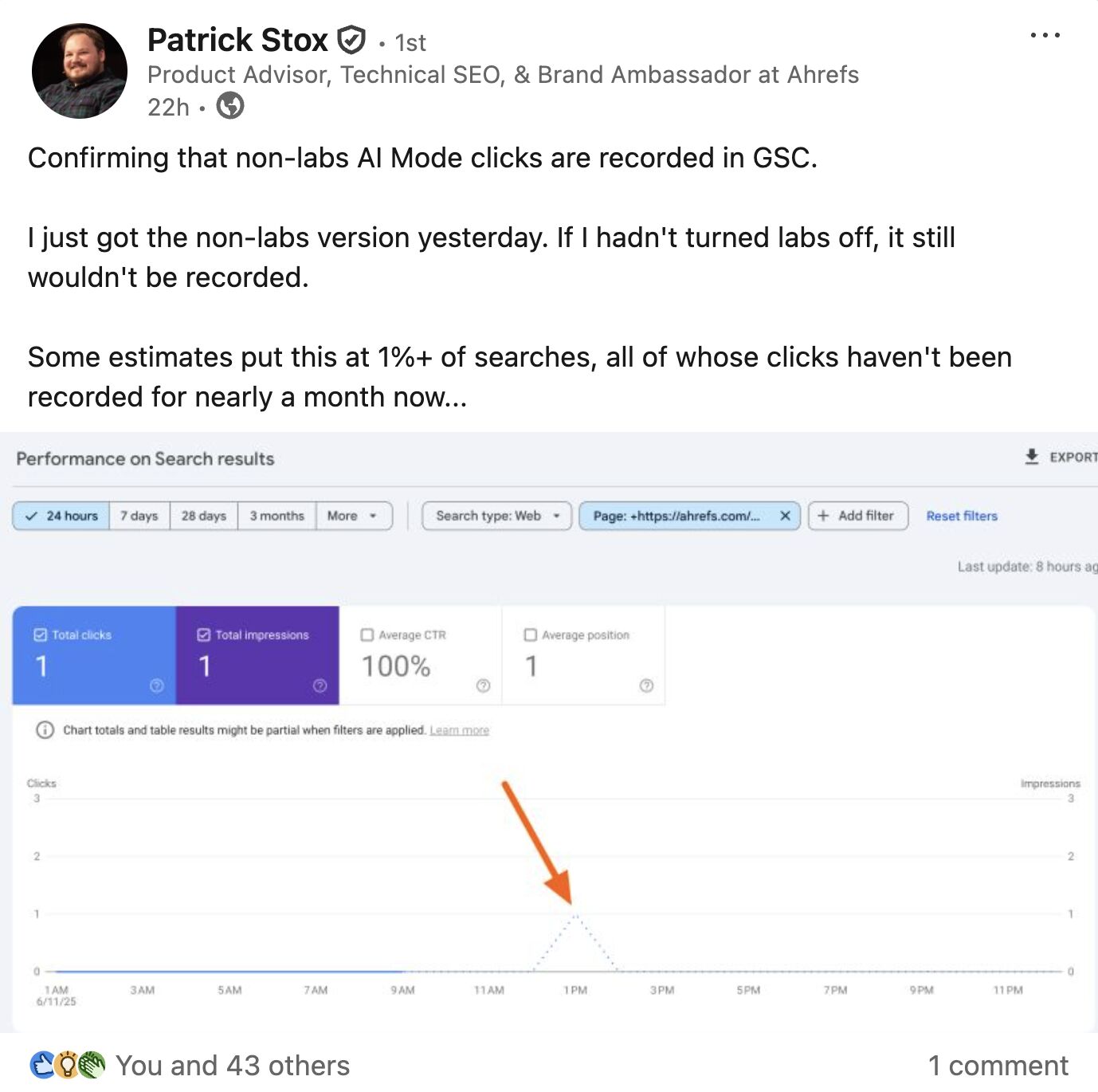
You can only track AI Overviews as position one in Google Search Console–meaning, you can’t disambiguate clicks from AI Overviews vs. traditional search clicks.
Google Search Console now enables click tracking in AI Mode but, as with AIOs, you won’t be able to compare those clicks against traditional search or any other Google property.
So, how else can you track zero-click search?
Here are a few ideas…
Track brand mentions in AI Overviews with Ahrefs Brand Radar
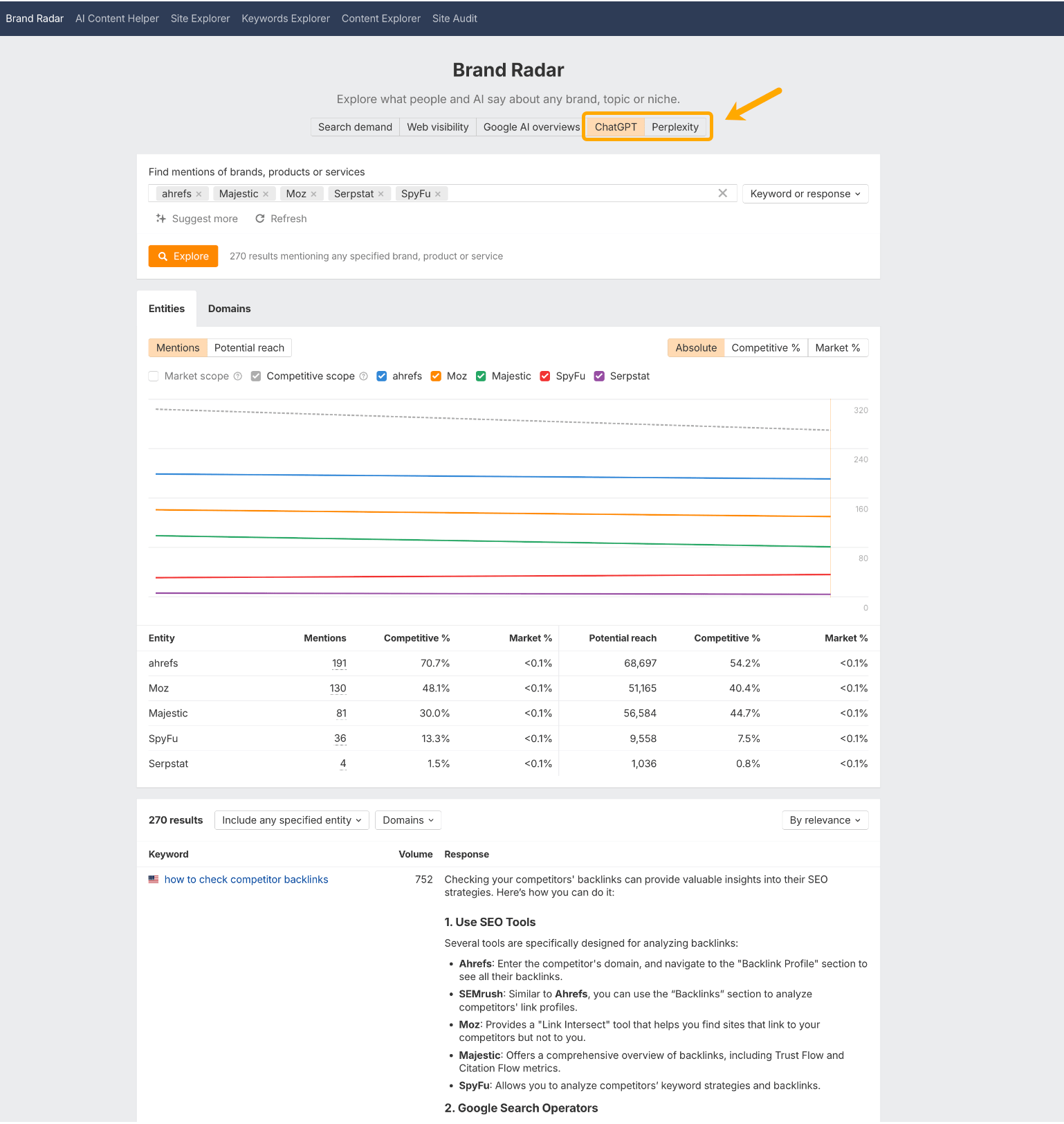
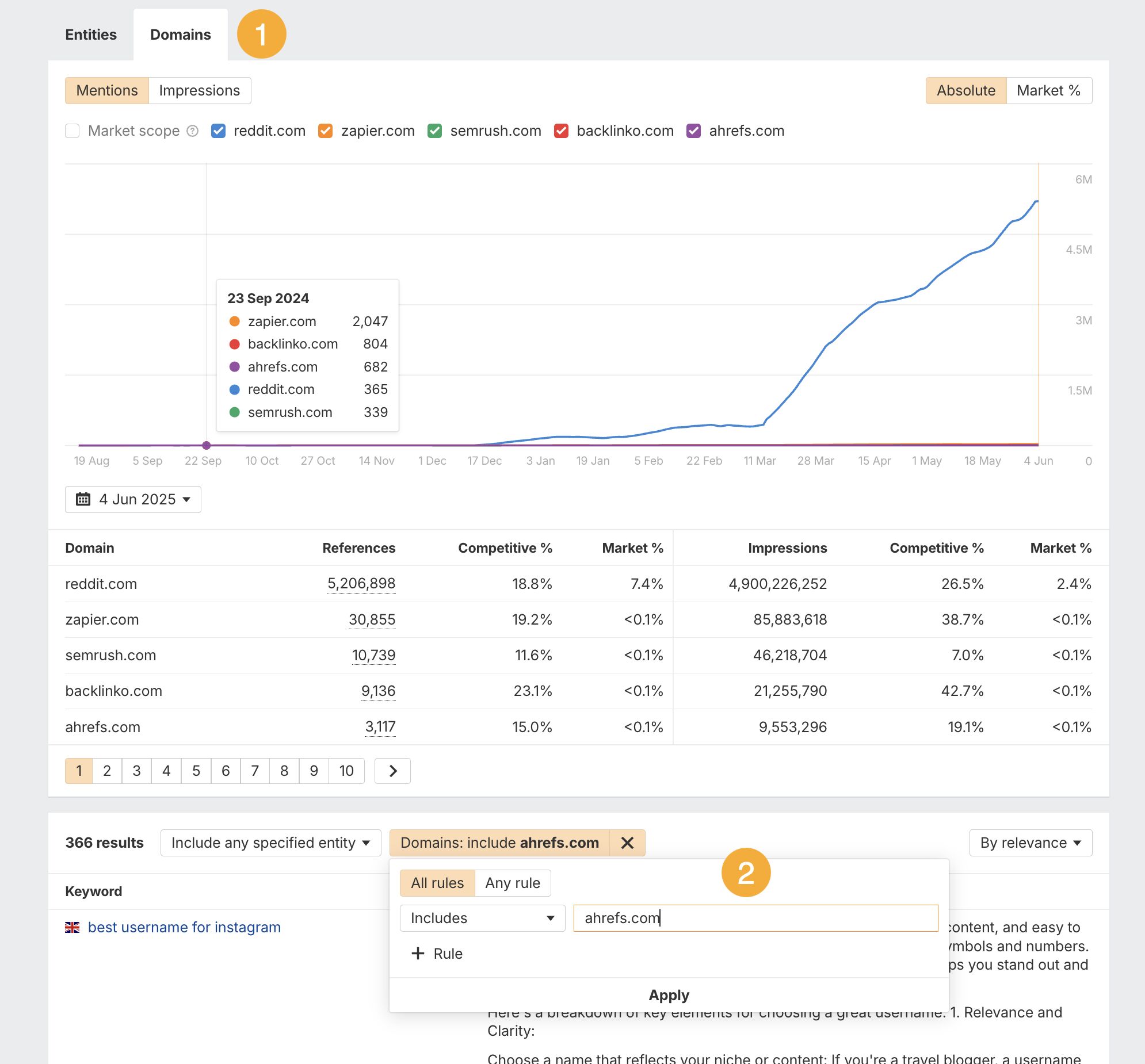
You can keep tabs on your AI Overview ownership with Ahrefs Brand Radar.
This tool lets you track mentions of your brand–not only in the queries that lead to an AI Overview–but in AI Overviews themselves.
Do a simple search for your brand name in keywords or AI Overviews to work out your total ownership.
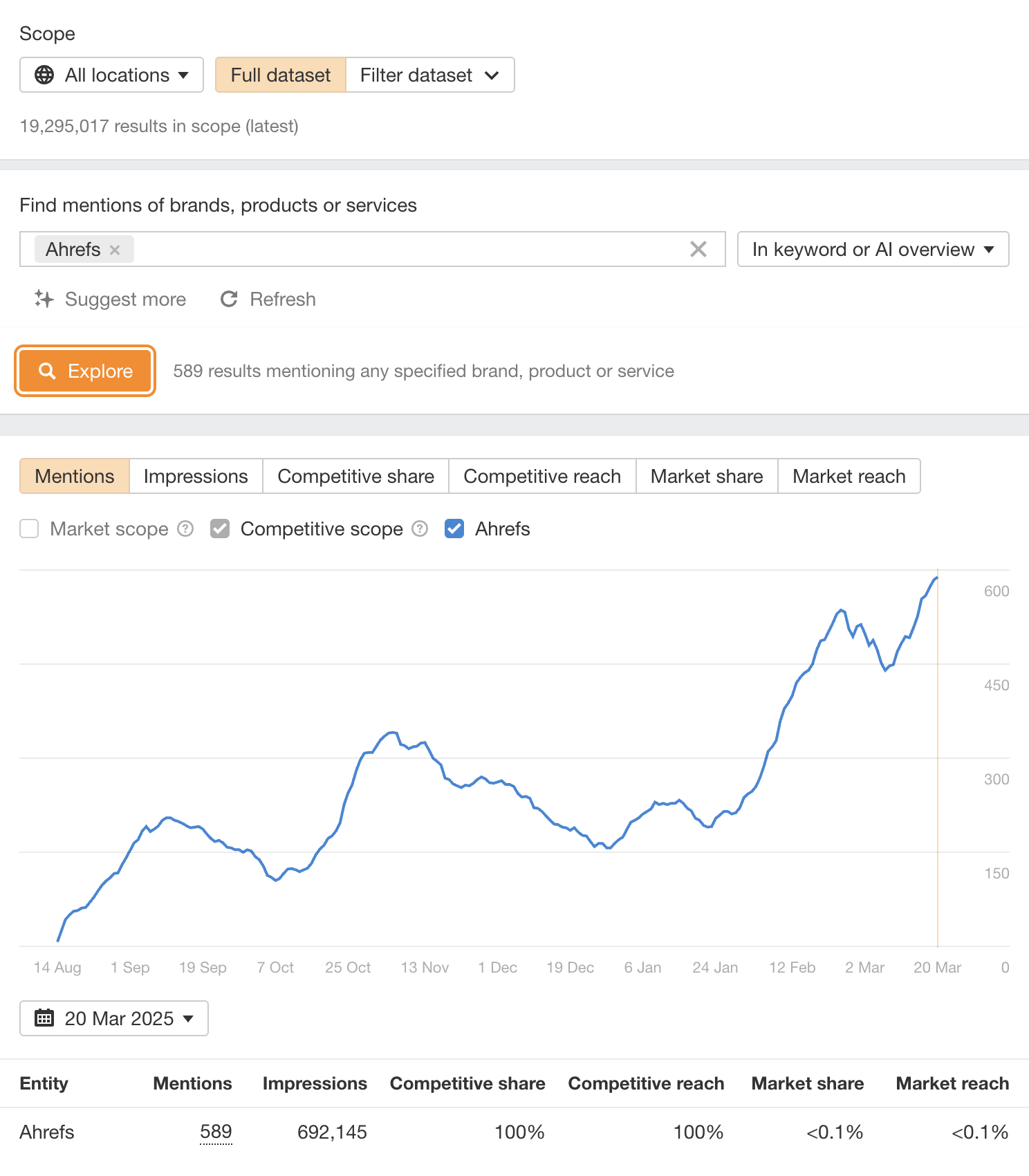
Then scroll down further to view mentions in-situ, and see which domains are commonly linked in zero-click search answers.
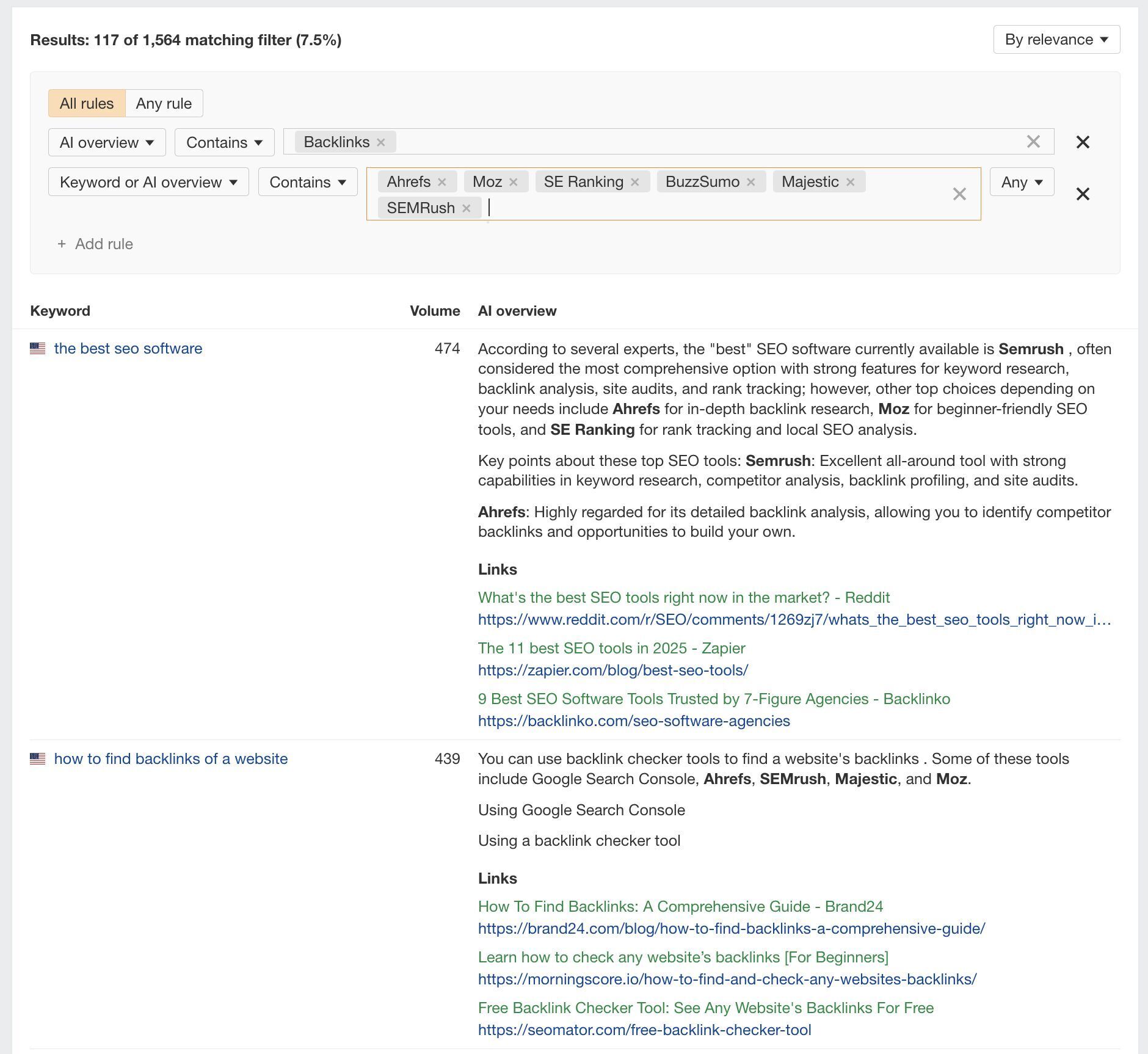
You can search for your specific site to see all the AI Overviews you’re currently cited in via the “Domains” tab.
Track your mentions in AI with Ahrefs Brand Radar
AI and zero-click search summarizes your content, making it tricky to keep tabs on.
But your brand name is a constant.
For that reason, many marketers are turning to AEO tools to monitor mentions of their brand, and brand associations in AI platforms.
You can track instances of your brand in prompts and AI responses across ChatGPT and Perplexity, using Ahrefs Brand Radar.
Watch your traffic in Ahrefs Web Analytics
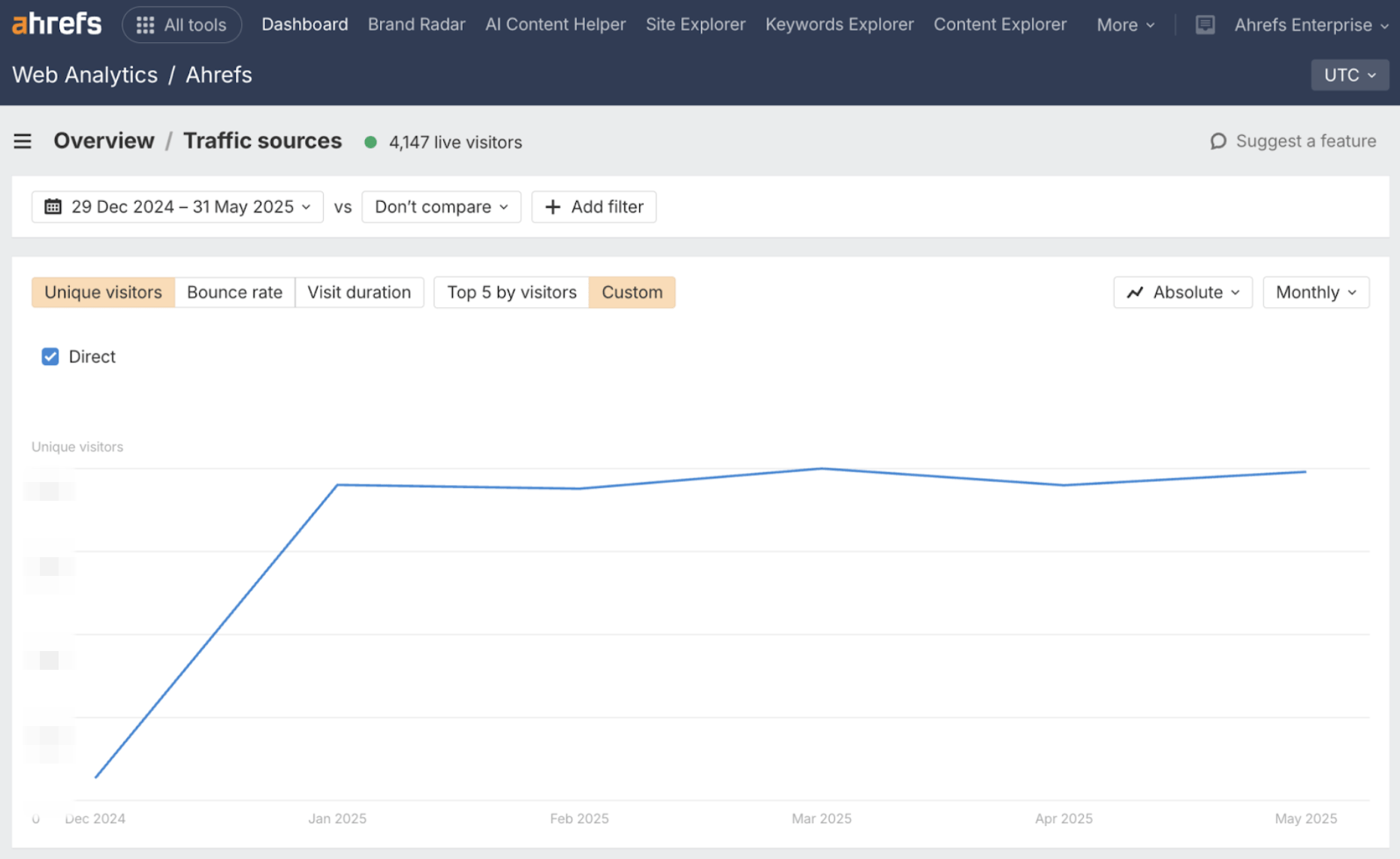
Zero-click search doesn’t actually mean zero clicks–just far fewer than we’ve been used to.
You can use our free Web Analytics tool to understand where traffic is going now, and what engages users when they do click.
According to our latest research, zero-click searchers are most likely to land on branded content ¹ ².
If you spot any uplift in direct traffic or homepage growth, this can signal increased brand recall—users might search your brand name after seeing your answer in a snippet, or visit your brand pages after getting further down the funnel in AI.
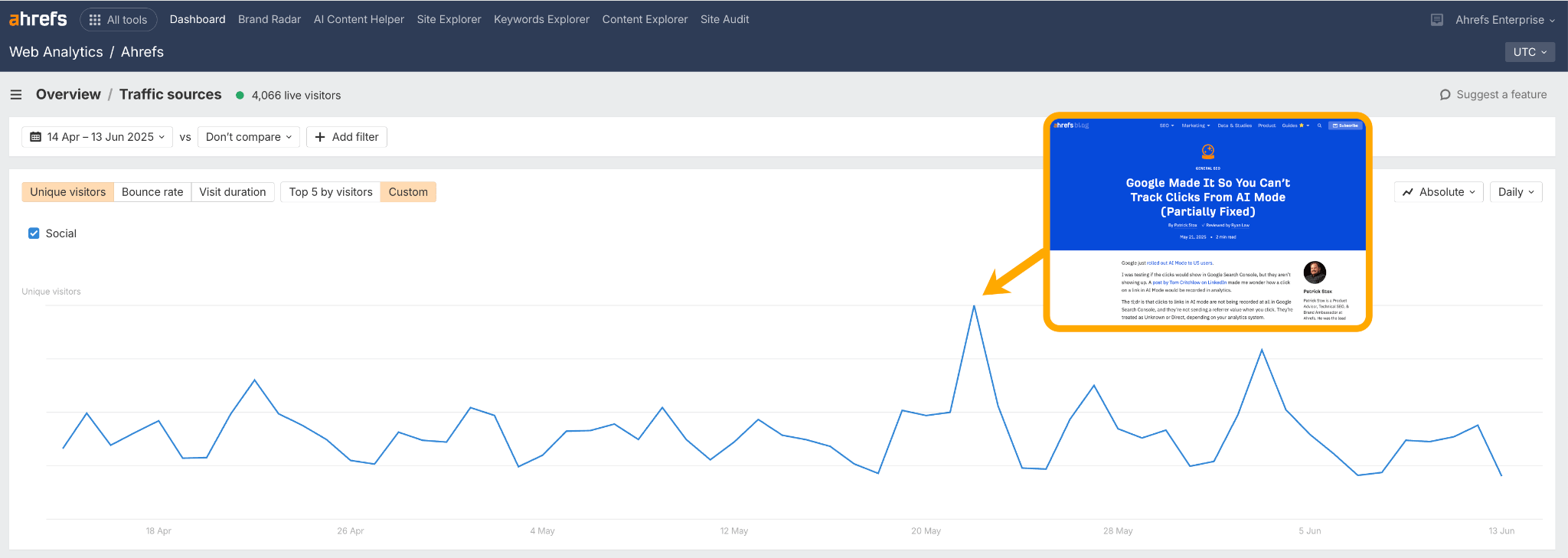
You can also monitor your referral and social traffic to understand which pieces of content are leading to word-of-mouth or social sharing.
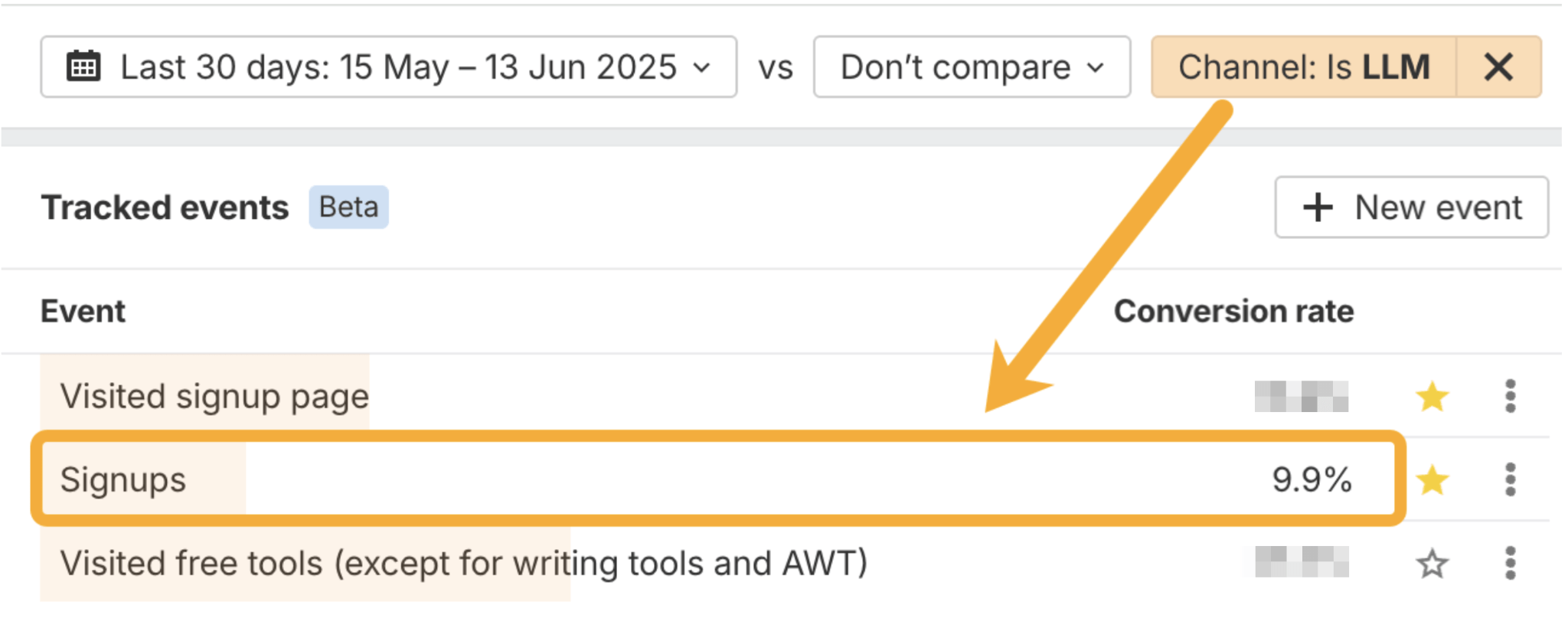
And track conversions to find out which channel is driving the most bottom-line value.
For instance, I recently noticed our AI conversion rate has shot up to ~10% in the past couple of months–the highest of any of our channels–according to custom, tracked events of our signups.
Start tracking now—you may find some channels massively outperforming your assumptions.
Where do we go from here?
So, that’s zero-click search…
But we’re moving beyond even that.
Post-click search is the next threat to our traffic. AI agents don’t just answer for you—they act for you. Filling in forms. Running scripts. Using your product. All without the user ever setting foot on your site.
But I digress.
The important thing to remember is that clickless search is the new business model. Fighting it won’t work. Working around it might.
Not everything you publish will earn a click, but it might still earn a mention or a moment of influence.
We don’t need to quit search, but we need to stop overrelying on it–diversification is the only way forward.
The best-case scenario might just be visibility without attribution, which we’ll just have to be fine with.
No one’s coming to save us, but marketers are famously good at adapting, and this is just one more pivot.